Figure 1, The steps of regenerative medicine. - StemBook - NCBI

The production of cellular therapies requires the optimization of four steps: first, isolating and culturing cells that can be readily obtained from a patient in a non-invasive fashion. Second, the reprogramming of these cells into a pluripotent state. Third, the directed differentiation of those patient-specific pluripotent cells into the cell type relevant to their disease. And, fourth, techniques for repairing any intrinsic disease-causing genetic defects and transplantation of the repaired, differentiated cells into the patient. Notably, these disease-relevant patient cells can also be used for in vitro disease modeling which may yield new insights into disease mechanisms and drug discovery.
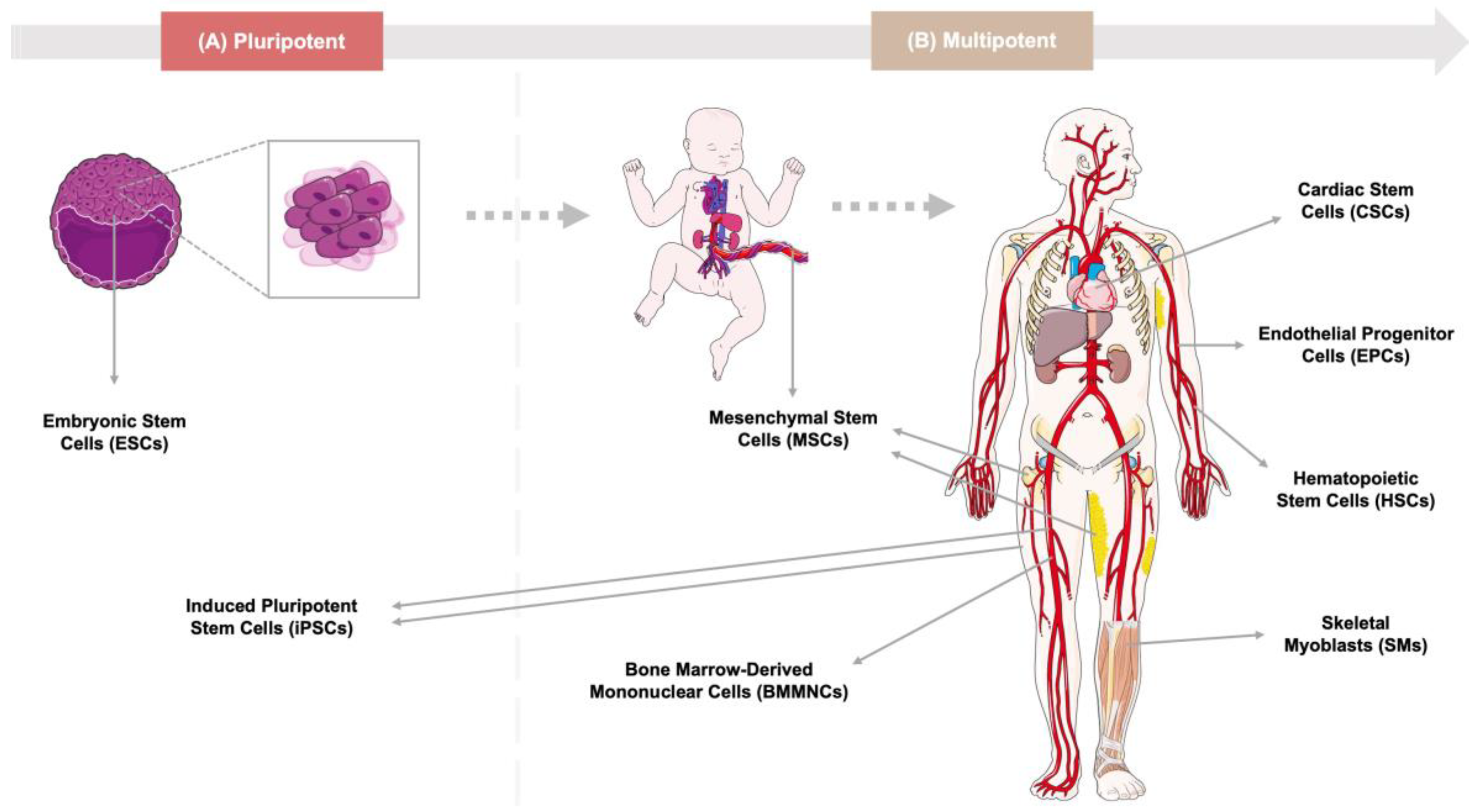
Cells, Free Full-Text

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Robust generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human embryonic

Feeder-independent culture protocol – EDTA splitting - StemBook
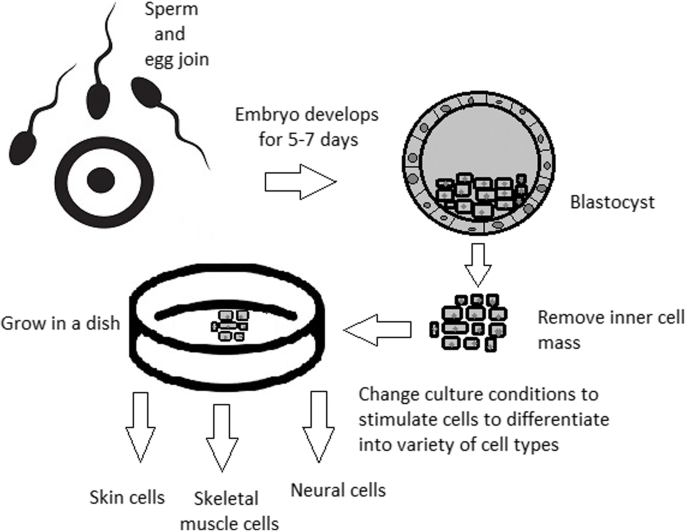
Stem cells: past, present, and future

Imaging transplanted stem cells in real time using an MRI dual

Commercialization, IPR, and Market of Stem Cell Products

Protocol for directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem

Liver development - StemBook - NCBI Bookshelf

Figure 1, The steps of regenerative medicine. - StemBook - NCBI

Differential role of natural killer group 2D in recognition and
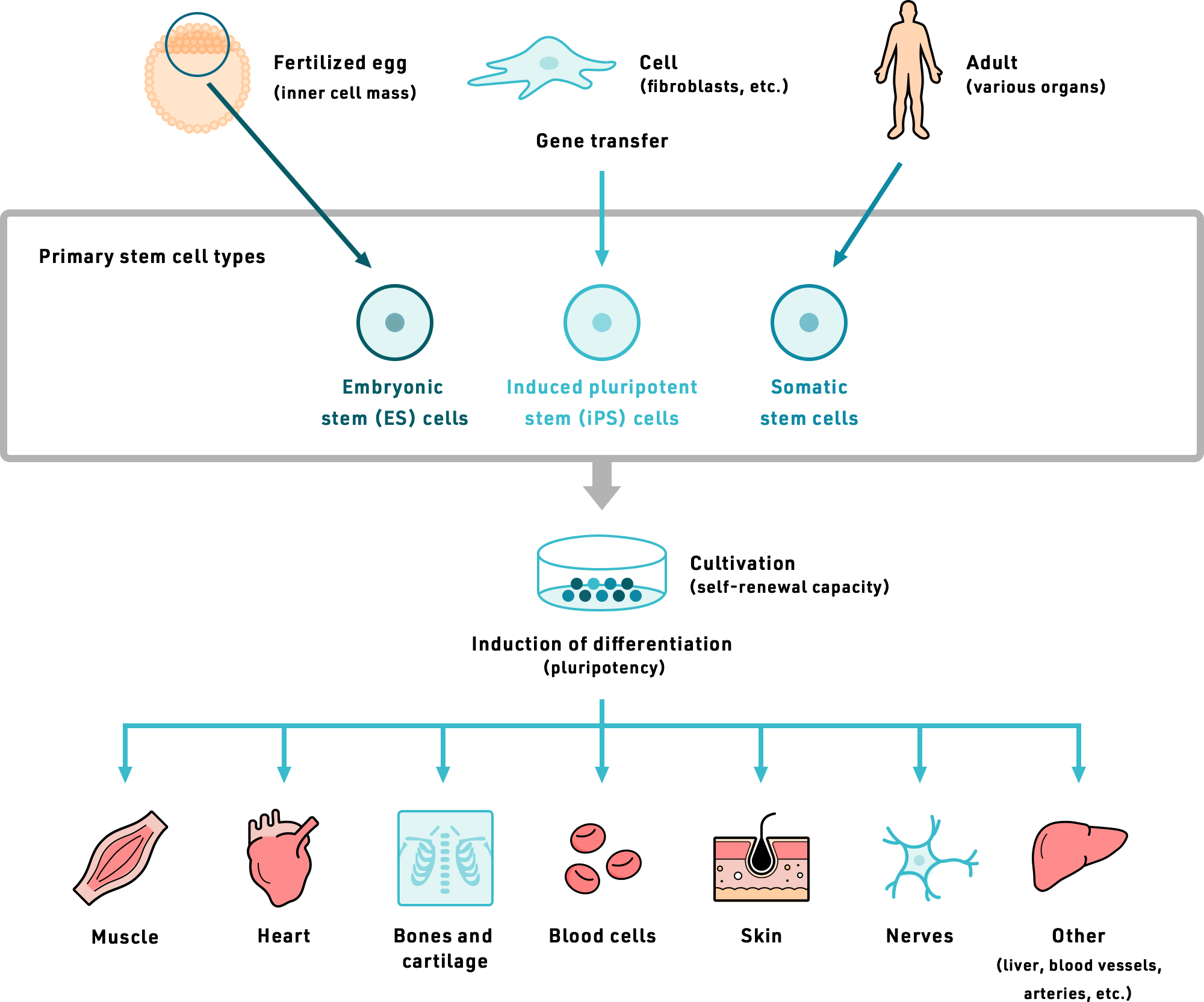
Regenerative Medicine SanBio - Official Site

The two strategies of stem cell application in regenerative

Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture Scale-Out - Assay Guidance Manual

Is Regenerative Medicine Ready for Prime Time in Diabetic