Chapter 3 Love in Relationships. Chapter Outline Descriptions of Love Love in Social and Historical Context Theories on the Origins of Love How Love Develops. - ppt download

True or False? College students report that they are more likely to make relationship decisions with their heart than their head.
Chapter 3 Love in Relationships
Chapter Outline Descriptions of Love Love in Social and Historical Context Theories on the Origins of Love How Love Develops in a New Relationship Love as a Context for Problems Jealousy in Relationships
College students report that they are more likely to make relationship decisions with their heart than their head..
Answer: True College students report that they are more likely to make relationship decisions with their heart than their head.
True or False Undergraduate women are more likely than men to believe that jealousy shows love.
Answer: False Women were significantly more likely than men to disagree or to strongly disagree that jealousy shows how much your partner loves you : 63.2% of the women, in contrast to 42.6% of the men, disagreed with the statement.
Heavy women who lose weight are more likely to become involved in a romantic relationship..
Answer: True Heavy women who lose weight are more likely to become involved in a romantic relationship.
Realistic Love Romantic Love: –Characterized by such beliefs as love at first sight, there is only one true love, and love conquers all. –Symptoms of romantic love include drastic mood swings, palpitations of the heart, and intrusive thoughts about the partner..
–Conjugal (married) love is less emotional, passionate, and exciting than romantic love and is characterized by companionship, calmness, comfort, and security..
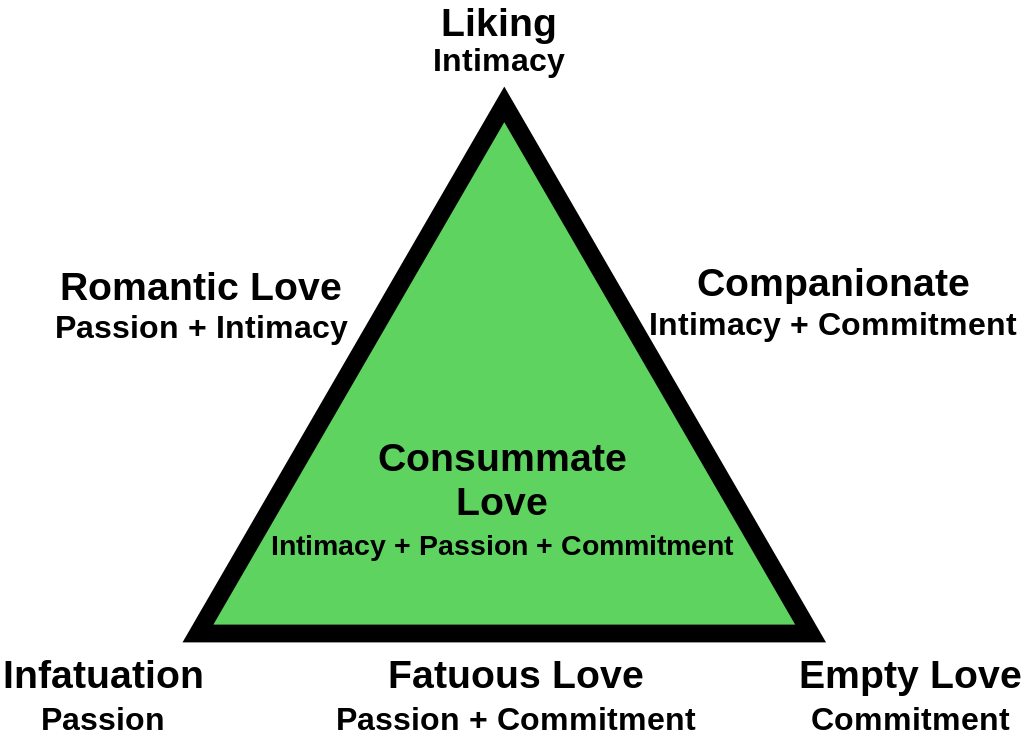
Triangular View of Love Sternberg’s triangular view of love consists of three basic elements: –Intimacy –Passion –Commitment The presence or absence of these provides a description of types of love.
Nonlove: –Absence of intimacy, passion, and commitment Two strangers looking at each other from afar have a nonlove. 2. Liking: –Intimacy without passion or commitment A new friendship may be described in these terms of the partners liking each other..
Infatuation –Passion without intimacy or commitment Two persons flirting with each other in a bar may be infatuated with each other. 4. Romantic love –Intimacy and passion without commitment Love at first sight reflects this type of love..
Companionate love –Intimacy and commitment without passion A couple who have been married for fifty years are said to have a companionate love. 6. Fatuous love –Passion and commitment without intimacy A couple who are passionately about each other and talk of the future but do not have an intimate connection with each other..
Empty love –Commitment without passion or intimacy A couple who stay together for social and legal reasons but who have no spark or sharing between them. 8. Consummate love –Combination of intimacy, passion, and commitment Sternberg’s view of the ultimate, all- consuming love..
They are happily married, have reared two children, and enjoy their lives together. Pg. 73.
B.intimacy, friendship, and commitment. C.intimacy, passion, and commitment. D.intimacy, compassion, and commitment..
Answer: C Steinberg s triangular view of love consists of three basic elements, which are intimacy, passion, and commitment.
Pragma –The love of the pragmatic, who is logical and rational. Eros –A love style of passion and romance..
Storge –A calm, soothing, nonsexual love devoid of intense passion. Agape –A love style that is selfless and giving..
A.ludic love B.agape love C.realistic love D.passive love.
Answer: C Realistic love is also known as conjugal love.
–Individuals attracted to someone of the same sex quickly feel the social and cultural disapproval of this attraction..
Buddhist Conception of Love The Buddhists conceived of two types of love: – unfortunate kind of love (self-love) –A good kind of love (creative spiritual attainment).
Agape –Based on a concern for the well-being of others. Spiritual, not sexual, in nature. Eros –Sexual love..
A.agape B.eros C.phileo D. good love.
Answer: C Phileo is based on friendship and can exist between or among family, friends, and lovers.
Marriages of the sons and daughters of the aristocracy were arranged with the heirs of other states with whom an alliance was sought..
A.Greeks B.Romans C.Christians D.Buddhists.
Answer: A The Greeks introduced three concepts of love: phileo, agape and eros.
Learning Theory –Emphasizes that love feelings develop in response to certain behaviors occurring in certain contexts..
The stages of love include rapport, self revelation, mutual dependency, and personality need fulfillment. Psychosexual Theory –Love results from blocked biological sexual desires..
Attachment Theory –Emphasizes that a primary motivation in life is to be connected with other people..
Learning Does not account for why some people will share positive experiences yet will not fall in love and why some people stay in love despite negative behavior..
Ego-Ideal Does not account for the fact that people of similar characteristics fall in love..
Doesn’t account for homosexual love. Biochemical Does not specify how much of what chemicals result in the feeling of love. Attachment Some people prefer to be detached..
A.evolutionary theory B.attachment theory C.learning theory D.ontological theory.
Answer: C Learning theory emphasizes that love feelings develop in response to certain behaviors occurring within certain contexts.
A.psychosexual theory B.learning theory C.evolutionary theory D.ontological theory.
Answer: D Ontological theory states that love arises from a lack of wholeness in our being.
Probability of being in a relationship is influenced by the cultural ideal of physical appearance. Self-esteem and self-disclosure are associated with the development of healthy love relationships. The individual must be physiologically aroused..
2. It allows one to feel generally equal to others. 3. It allows one to take responsibility for one’s own feelings, ideas, mistakes, and failings. 4. It allows for the acceptance of strengths and weaknesses in one’s self and others..
It allows one to validate one’s self and not to expect the partner to do this. 6. It permits one to feel empathy 7. It allows separateness and interdependence, as opposed to fusion and dependence..
Some people report being in love with two people at the same time. Some are in love with someone who is emotionally or physically abusive..
–Some research suggests that individuals in love make risky/dangerous/questionable decisions..
–It may involve following a victim; threats of physical harm to the victim, one’s self, or another person; or restricting the behavior of the victim, including kidnapping or home invasion..
–A lack of emotional and/or sexual interest in the primary partner..
Internal Causes of Jealousy Mistrust Low self-esteem Being involved and dependent Lack of perceived alternatives Insecurity
The opposite of jealousy..
Polyamory is more emotionally intimate than swinging and offers the possibility of greater gender equality than polygyny because both men and women can have more than one partner..
Those who practice polyfidelity expect their partners to remain sexually exclusive within a group larger than two people..
They also have similar relationships with others. They note that no one person can be all things to another. Pg. 93.
–Vees are three-person relationships in which one member is sexually connected to the two others. –A triad includes three sexually involved adults..
–Moresomes, groups with five or more adult members, are larger, more fragile, and more complicated than quads..
Secondary partners frequently maintain separate finances and residences, and while they may discuss major life decisions, they generally do not make decisions jointly..
Some poly families have spice, the poly word for more than one spouse..

100 Relationship Topics to Debate Based On Various Ideas

PPT - Chapter 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:5395117

Motivation Theories [5 Famous Motivation Theories]

All About Love Summary of Key Ideas and Review
Love and Relationships – Human Development

Chapter 3 Love in Relationships. Chapter Outline Descriptions of Love Love in Social and Historical Context Theories on the Origins of Love How Love Develops. - ppt download

Love
Chapter 3. Assessing Community Needs and Resources, Section 14. SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, Main Section

4 Child Development and Early Learning, Transforming the Workforce for Children Birth Through Age 8: A Unifying Foundation

The Four Loves Chapter 3: Affection Summary & Analysis

The Art Thief by Michael Finkel: 9780525657323

Relationship Smarts PLUS 5.0 - The Dibble Institute

Chapter 3 Love in Relationships. Chapter Outline Descriptions of Love Love in Social and Historical Context Theories on the Origins of Love How Love Develops. - ppt download







