Copper accumulation, translocation, and toxic effects in grapevine cuttings

PDF] Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: Rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity.
Frontiers Fungicides and the Grapevine Wood Mycobiome: A Case Study on Tracheomycotic Ascomycete Phaeomoniella chlamydospora Reveals Potential for Two Novel Control Strategies

Multi-omics analyses on the response mechanisms of 'Shine Muscat' grapevine to low degree of excess copper stress (Low-ECS) - ScienceDirect

Role of phytohormones in heavy metal tolerance in plants: A review - ScienceDirect

Plants, Free Full-Text

PDF] Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: Rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity.

Alleviation effects of magnesium on copper toxicity and accumulation in grapevine roots evaluated with biotic ligand models

Potential use of grapevine cv Askari for heavy metal phytoremediation purposes at greenhouse scale

Effects of Copper on Root Morphology, Cations Accumulation, and Oxidative Stress of Grapevine Seedlings

Understanding and managing nitrogen nutrition in grapevine: a review

Root system structure as a criterion for the selection of grapevine genotypes that are tolerant to excess copper and the ability of phosphorus to mitigate toxicity - ScienceDirect

Multi-omics analyses on the response mechanisms of 'Shine Muscat' grapevine to low degree of excess copper stress (Low-ECS) - ScienceDirect

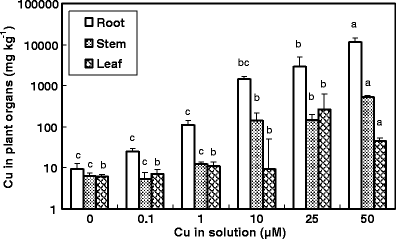
Figure 1.3 from Copper impacts in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): molecular, biochemical and biotechnological approaches

Figure 1.3 from Copper impacts in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): molecular, biochemical and biotechnological approaches
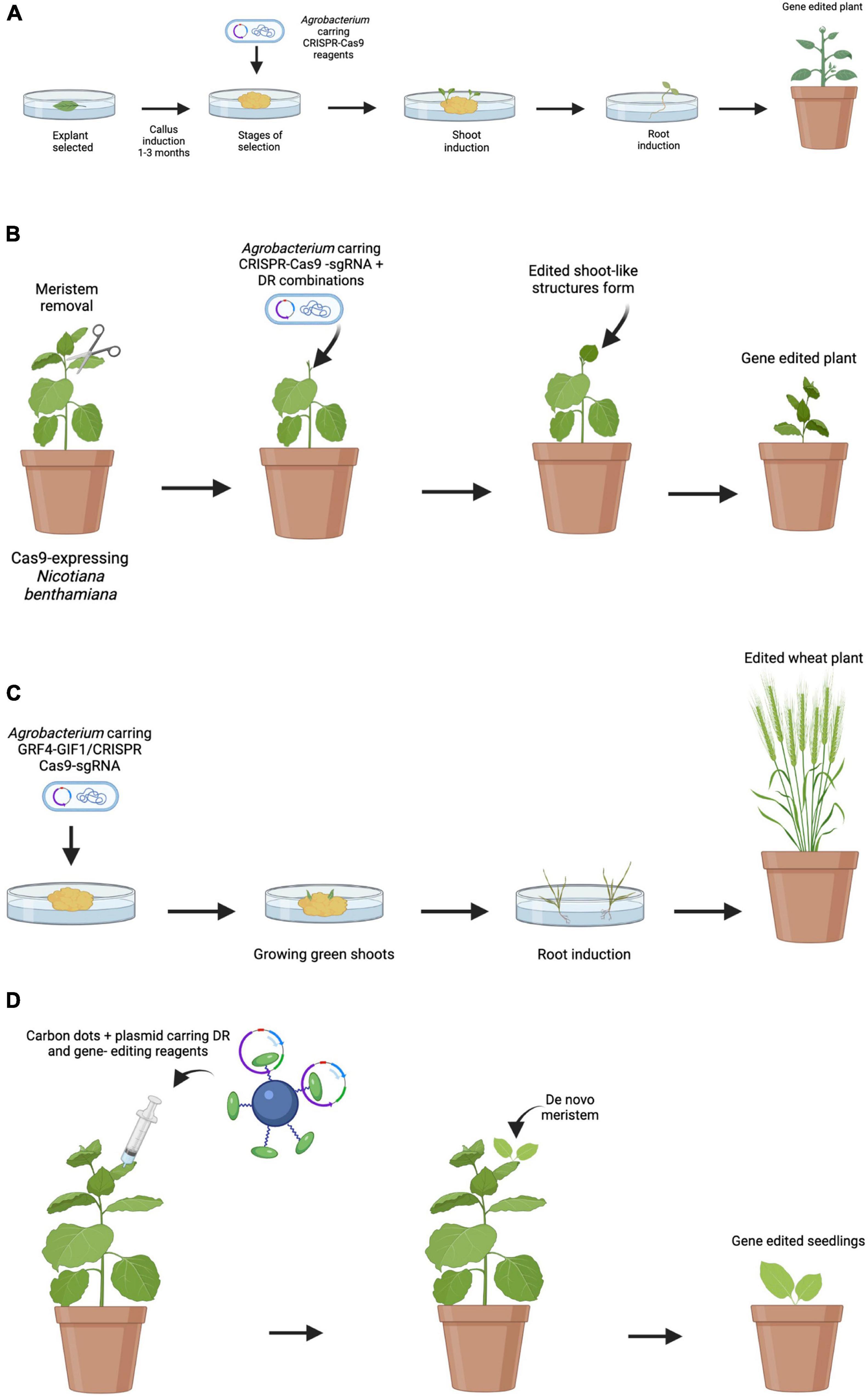
Frontiers New Technologies and Strategies for Grapevine Breeding Through Genetic Transformation







