Many signal processing algorithms require computation of the derivative of a signal in real-time. Some of the examples are timing recovery, carrier frequency synchronization, FM demodulation and demodulation of LoRa signals. An analog or digital filter that computes such a derivative is known as a differentiator. Before we design such a discrete-time differentiating filter, let us review some of the fundamentals. A Derivative The following quote is attributed to Heraclitus, a Greek philosopher, from 535 BC. Change is the only constant in life. This was brought into the realm of science by Newton and Leibniz. The purpose of science is

Linear time-invariant system - Wikipedia
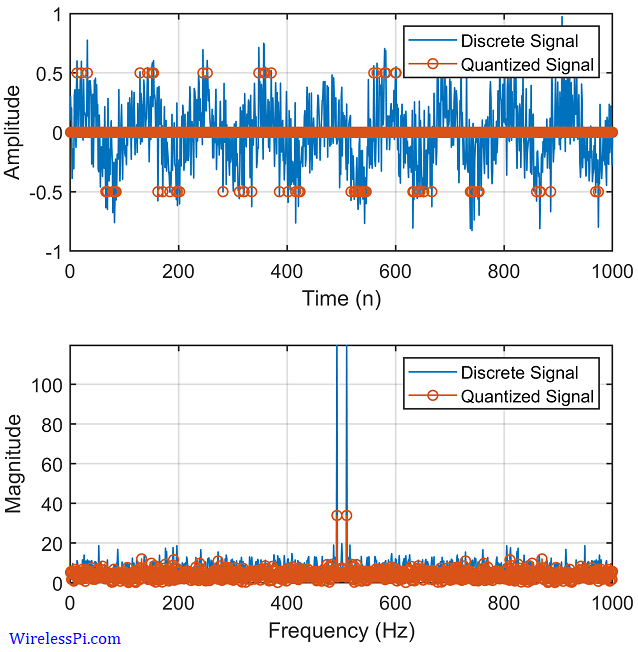
Noise is Not Always the Enemy
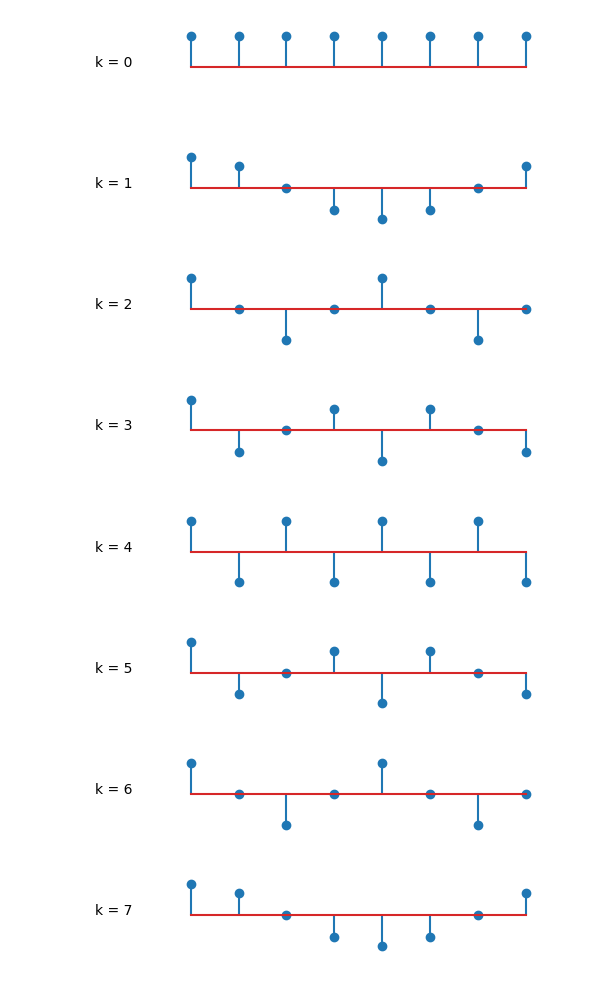
3.4. Discrete Time Fourier Series — Signal Processing 1.1
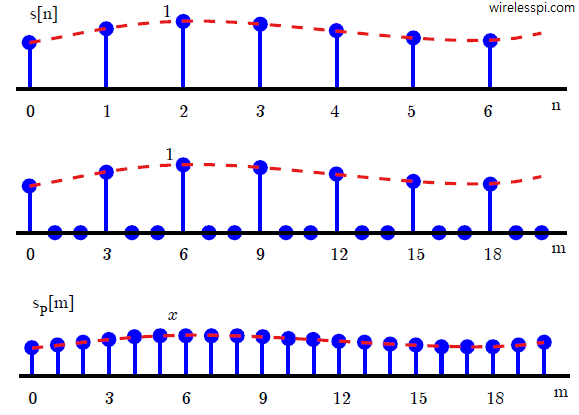
Sample Rate Conversion
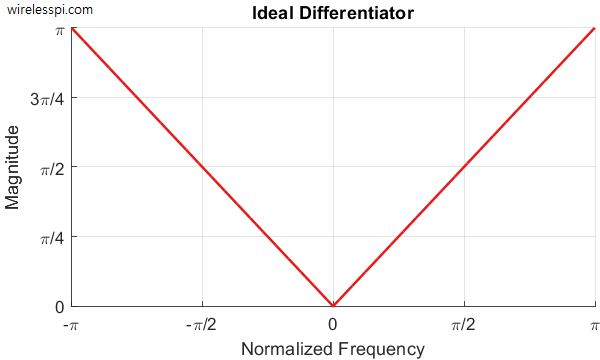
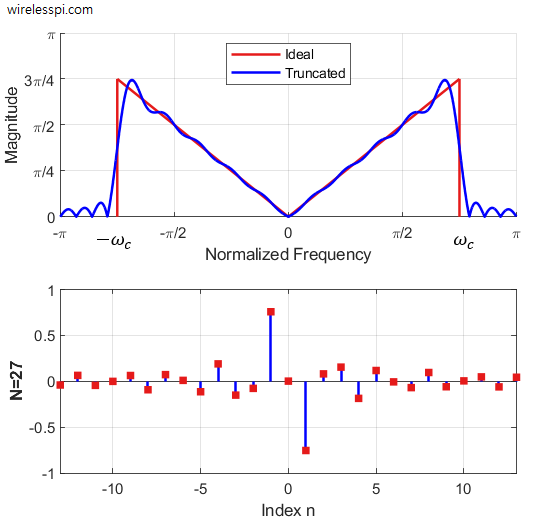
Design of a Discrete-Time Differentiator
14.3 Differentiators – Avionics II
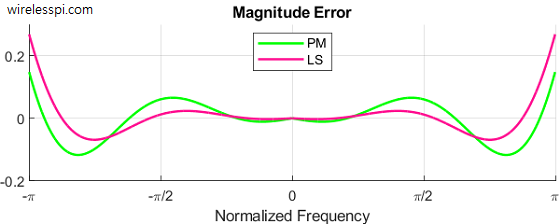
Design of a Discrete-Time Differentiator

Basic Operations in Signal Processing: Multiplication

Frequency Domain Representation of Discrete-Time Signals and
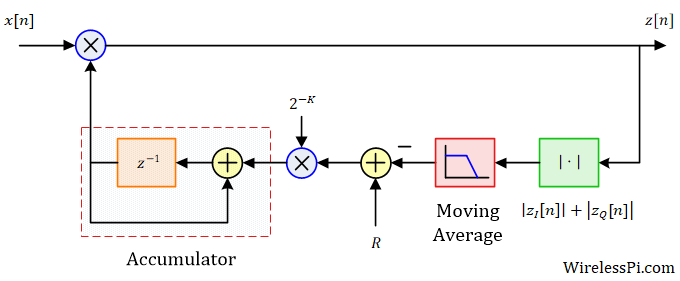
How Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Works
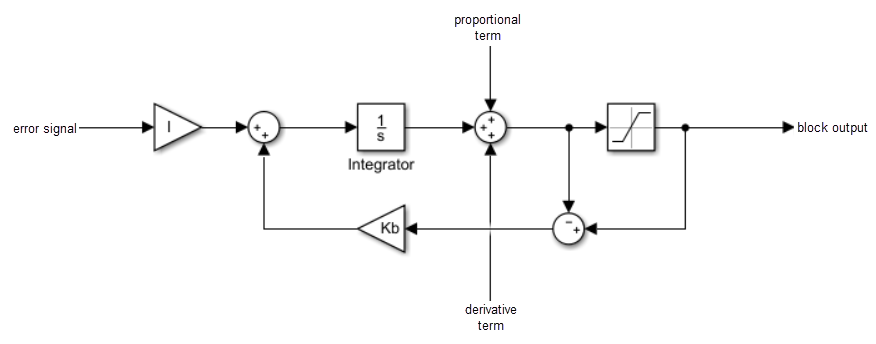
Discrete-time or continuous-time PID controller - Simulink
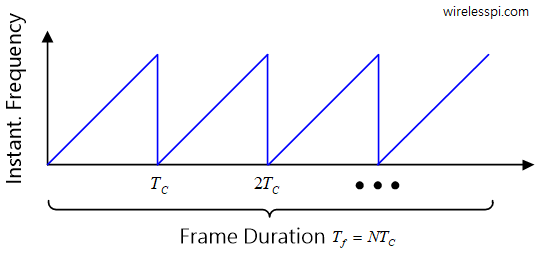
FMCW Radar Part 3 - Design Guidelines

Generative design of large-scale fluid flow structures via steady-state diffusion-based dehomogenization