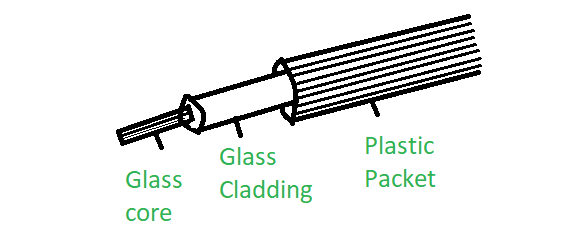
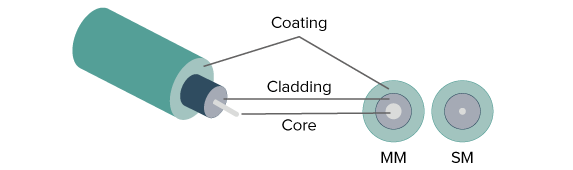
Optical Fiber Tutorial - Optic Fiber - Communication Fiber – Fosco
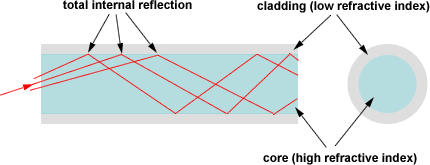
Basic Terms Refraction of light As a light ray passes from one transparent medium to another, it changes direction; this phenomenon is called refraction of light. How much that light ray changes its direction depends on the refractive index of the mediums. Refractive Index Refractive index is the speed of light in a vacuum (abbreviated c, c=299,792.458km/second) divided by the speed of light in a material (abbreviated v). Refractive index measures how much a material refracts light. Refractive index of a material, abbreviated as n, is defined as n=c/v Snell’s Law In 1621, a Dutch physicist named Willebrord Snell derived the relationship between the different angles of light as it passes from one transparent medium to another. When light passes from one transparent material to another, it bends according to Snell's law which is defined as: n1sin(θ1) = n2sin(θ2) where

Fiber Optic Cables, Fiber Patch Cables
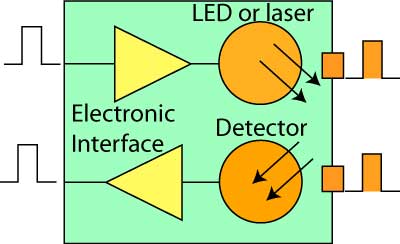
The FOA Reference For Fiber Optics - Fiber Optic Transmitters and
A typical point-to-point optical fiber communication link

Fiber Optics: Understanding the Basics

What are Fiber Bending Losses?

Fiber Optic Patch Cables Tutorial – Fosco Connect

The FOA Reference For Fiber Optics - Fiber Optic Network Design

How Optical Fibre Works

What Are Optical Fiber Core Size, Mode Field Diameter and
How to use a hand held fiber optic connector inspection microscope