Polymers, Free Full-Text
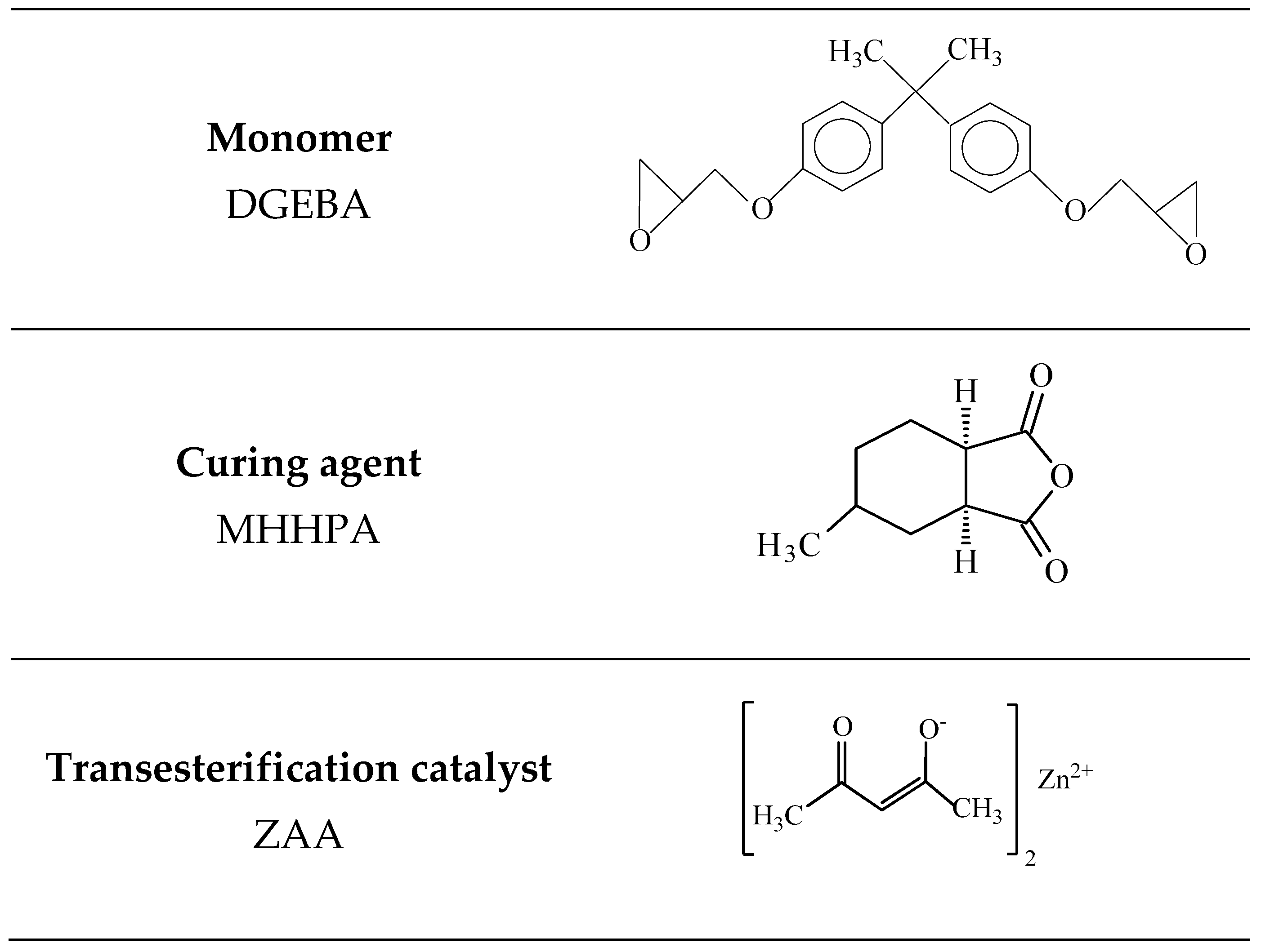
Epoxy/silica thermosets with tunable matrix (vitrimers) were prepared by thermal curing of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) in the presence of a hardener—4-methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride (MHHPA), a transesterification catalyst—zinc acetylacetonate (ZAA), and 10–15 nm spherical silica nanoparticles. The properties of the resulting material were studied by tensile testing, thermomechanical and dynamic mechanical analysis. It is shown that at room temperature the introduction of 5–10 wt% of silica nanoparticles in the vitrimer matrix strengthens the material leading to the increase of the elastic modulus by 44% and the tensile stress by 25%. Simultaneously, nanoparticles enhance the dimensional stability of the material since they reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion. At the same time, the transesterification catalyst provides the thermoset with the welding ability at heating, when the chain exchange reactions are accelerated. For the first time, it was shown that the silica nanoparticles strengthen welding joints in vitrimers, which is extremely important, since it allows to repeatedly use products made of thermosets and heal defects in them. Such materials hold great promise for use in durable protective coatings, adhesives, sealants and many other applications.
ACS Applied Polymer Materials Ahead of Print - ACS Publications
Polymers, Free Full-Text

PDF) TEXTBOOK OF POLYMER SC THIRD EDITION
Polymers, Free Full-Text
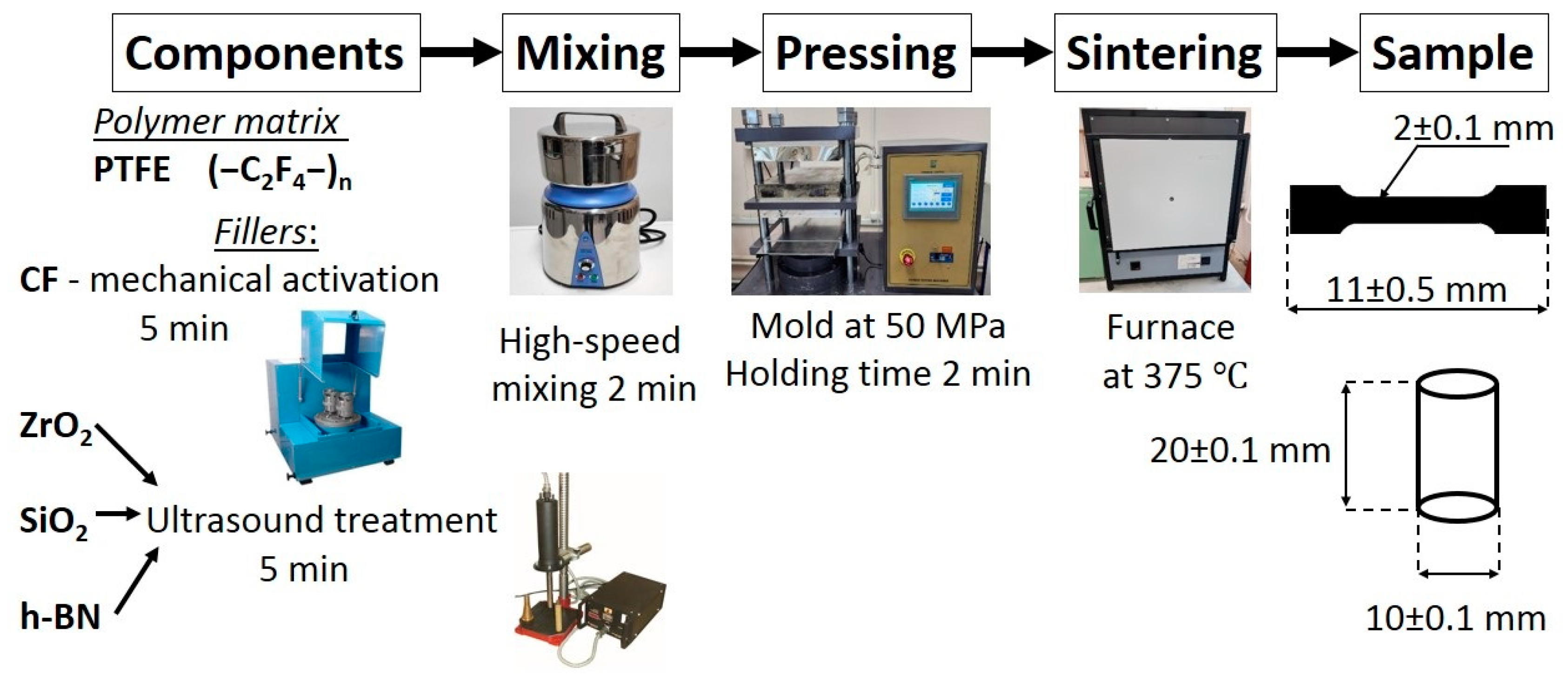
Polymers, Free Full-Text

SPE Polymers - Wiley Online Library

Home Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials

Polymer - BI without the BS

Molecularly designing polymer networks to control sound damping
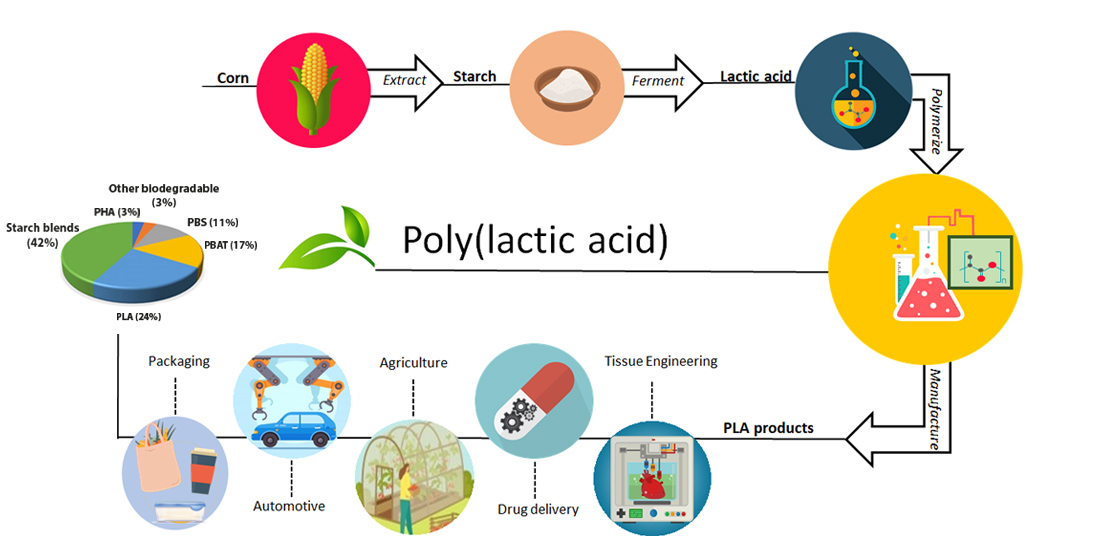
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Tacticity of Polymers, Overview & Types - Lesson











