The Sleeping Brain Suppresses External Inputs When Dreaming, But Not During All Sleep

To better understand how the brain protects itself from outside influences, researchers invited 18 participants to a morning nap in the lab.

Topographic-dynamic reorganisation model of dreams (TRoD) – A spatiotemporal approach - ScienceDirect
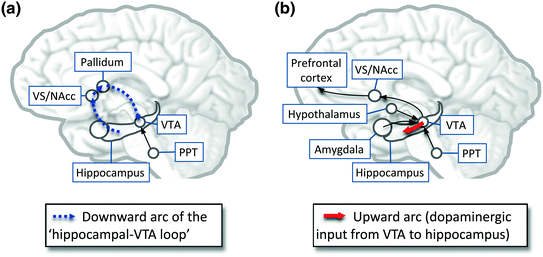
and Emotional Functions

Rapid eye movement sleep - Wikipedia
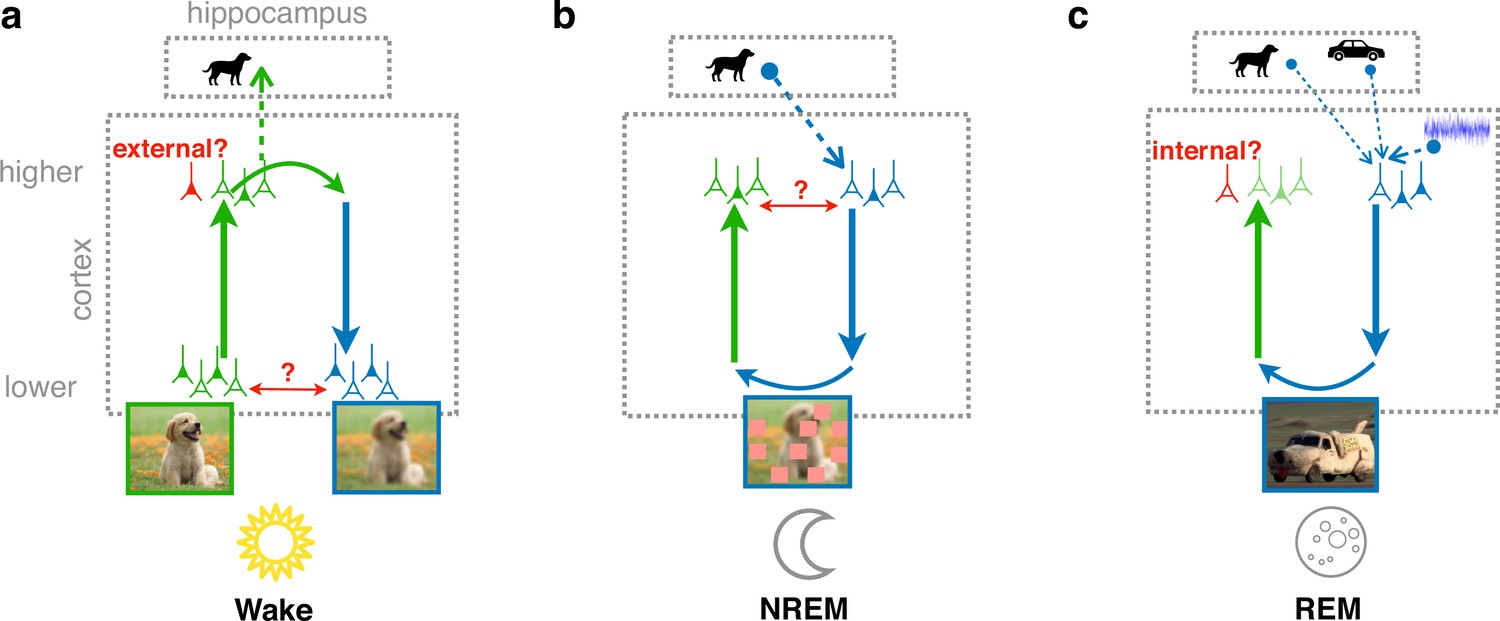
Learning cortical representations through perturbed and adversarial dreaming
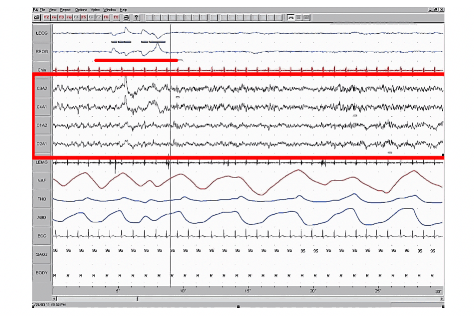
Dream a Little Dream – Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science

Sleep: The Wake-up Call You Need. If you're someone who sleeps less than…, by cure.fit, The .fit Way

Neuroscience of sleep - Wikipedia
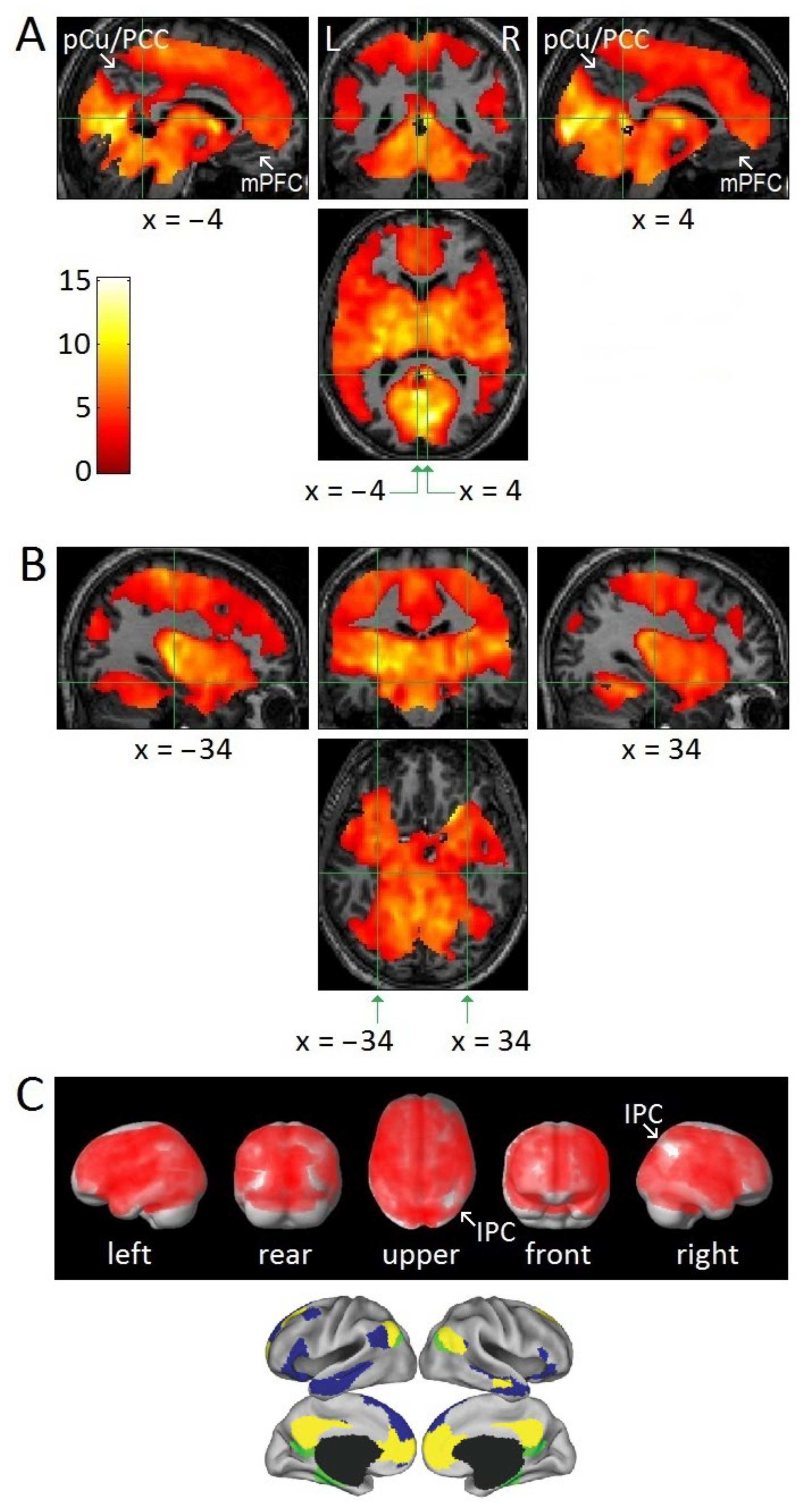
Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text

Neuro Science ShareTechnote
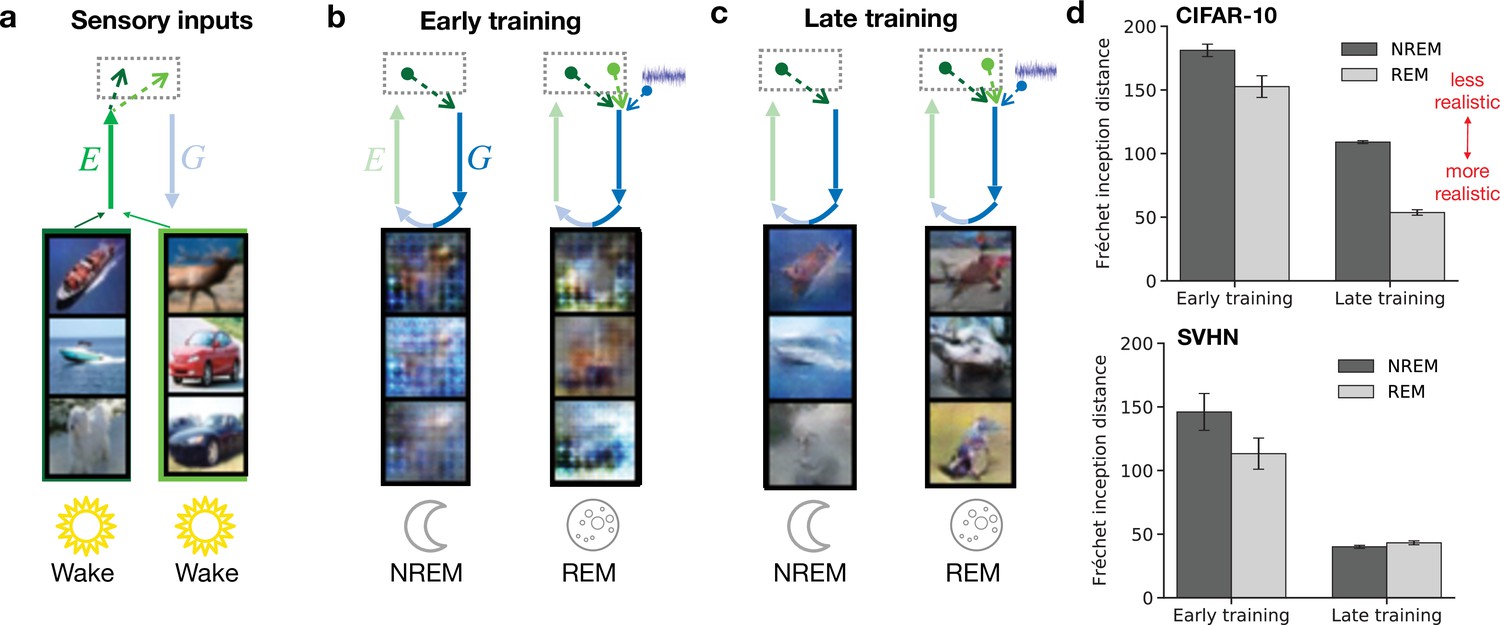
Learning cortical representations through perturbed and adversarial dreaming

Brain Control of Sleeping and Dreaming States An Excerpt from Where Buddhism Meets Neuroscience - Shambhala Pubs

The mysteries of sleep: everything we don't know about why we snooze - BBC Science Focus Magazine

Neuroimaging of Brain Oscillations During Human Sleep
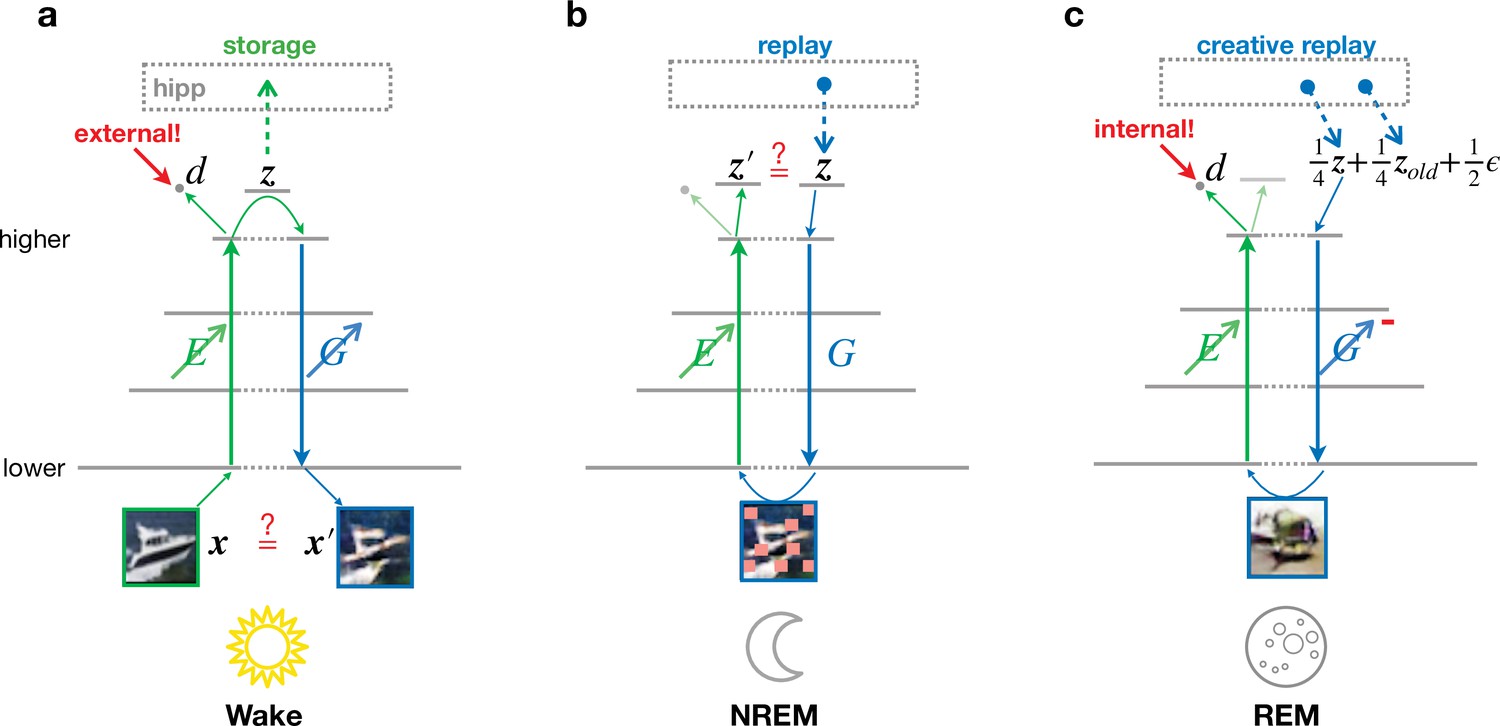
Learning cortical representations through perturbed and adversarial dreaming

Neurobiology and Neuropsychiatry of Sleep - Translational Aspects



















