The Postmenopausal Women - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
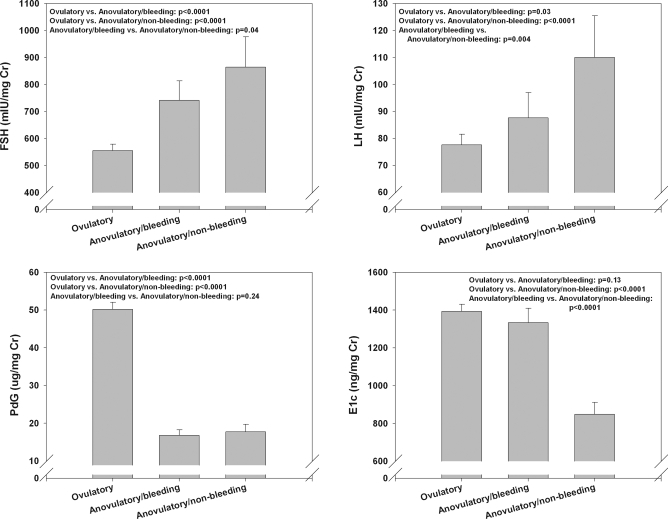
The menopausal transition marks a time of great variability in reproductive hormones, and this variability can be responsible for specific symptoms, such as hot flashes and mood disturbances. Once a woman who is more than 45 years old has gone for 12 months without a menstrual period, she is considered to be menopausal and has consistently low circulating estradiol and elevated gonadotropins. Estrogen is the most efficacious therapy for bothersome vasomotor symptoms. Although estrogen exerts clear-cut protective effects on the cardiovascular system in premenopausal women, medical evidence does not support its use for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Estrogen is generally not a first line agent for bone preservation in women without concurrent menopausal symptoms, despite its antiresorptive effects. Non-hormonal alternatives to estrogen and new, tissue specific estrogen complexes (TSECs) are now FDA approved and available for clinical use to treat common menopausal symptoms. For complete coverage of this and all related areas of Endocrinology, please visit our FREE on-line web-textbook, www.endotext.org.

Immune System Effects on the Endocrine System - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Fulltext Ajog v2 Id1045, PDF, Hormone Replacement Therapy

Case Study (Aub), PDF, Luteinizing Hormone
The Normal Menstrual Cycle and the Control of Ovulation - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Menopause, PDF, Estrogen

Paradigm Shift in Pathophysiology of Vasomotor Symptoms: Effects of Estradiol Withdrawal and Progesterone Therapy, PDF, Menopause

Evaluation and Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Chapters Archive - Page 34 of 45 - Endotext

Estrogen Therapy For Surgical Menopause IAPMD, 53% OFF

Premature Ovarian Insufficiency, PDF, Menopause