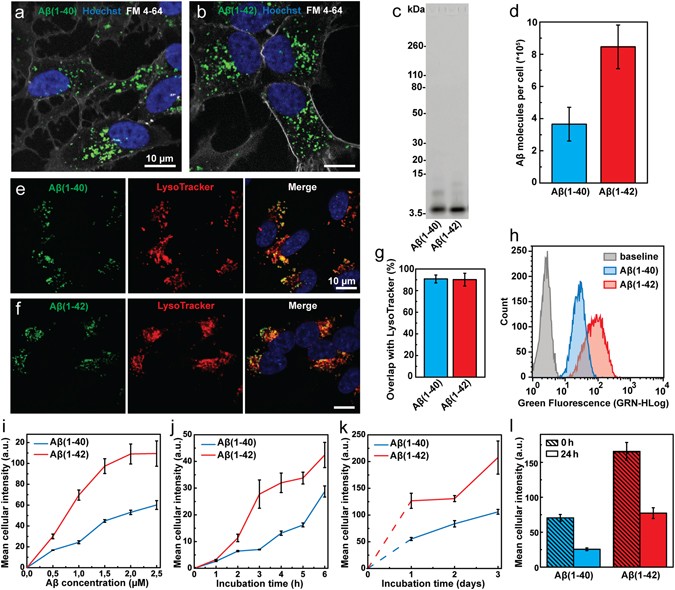
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ(1–40)

A delay in vesicle endocytosis by a C-terminal fragment of N-cadherin enhances Aβ synaptotoxicity

Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin- independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ (1–40)

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Human amyloid-β enriched extracts: evaluation of in vitro and in vivo internalization and molecular characterization, Alzheimer's Research & Therapy
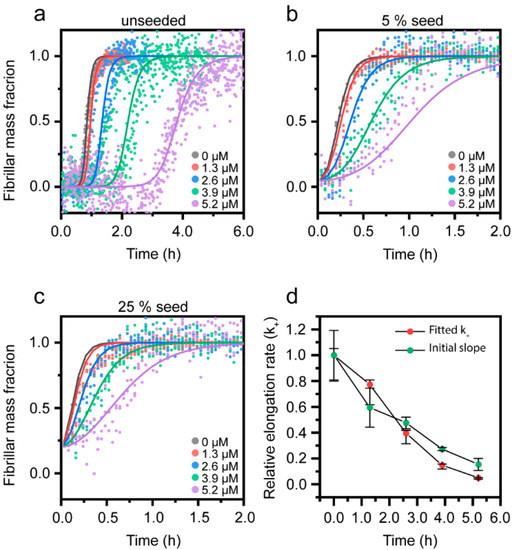
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text

Contribution of syndecans to cellular internalization and fibrillation of amyloid-β(1–42)

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect
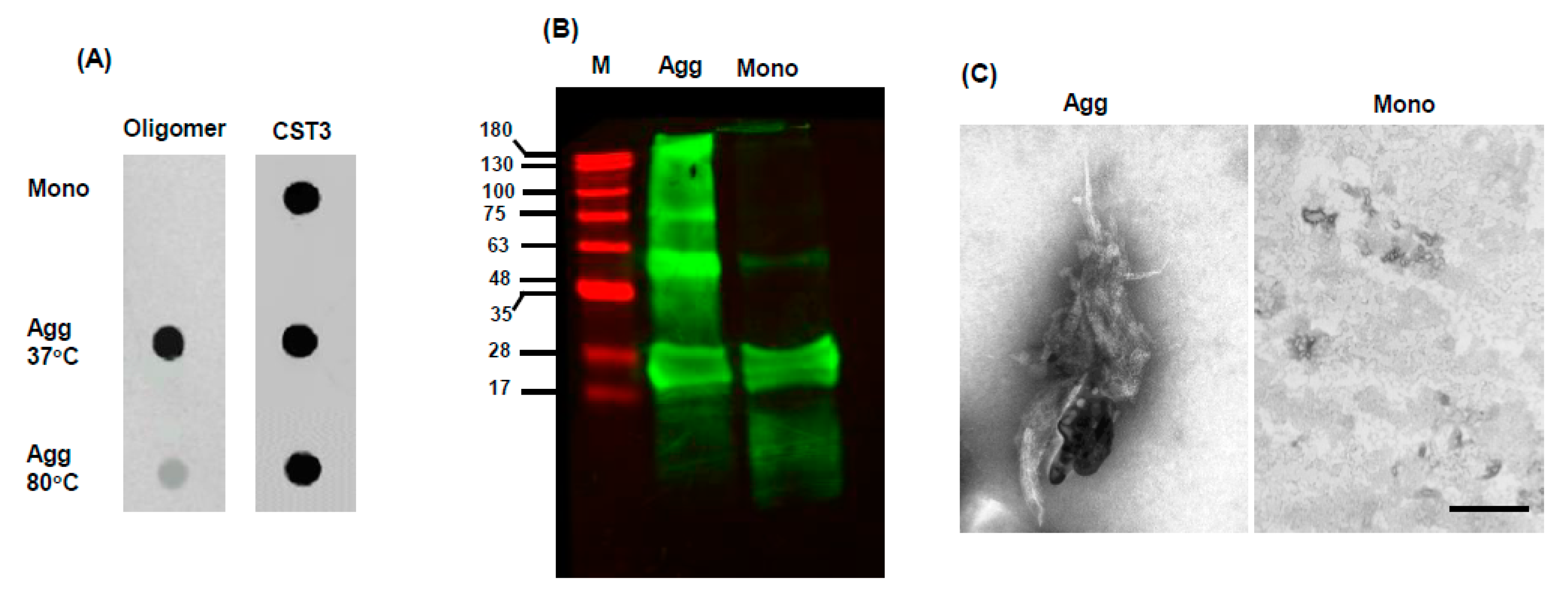
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Misfolded amyloid-β-42 impairs the endosomal–lysosomal pathway

Evidence for aggregation-independent, PrPC-mediated Aβ cellular internalization. - Abstract - Europe PMC
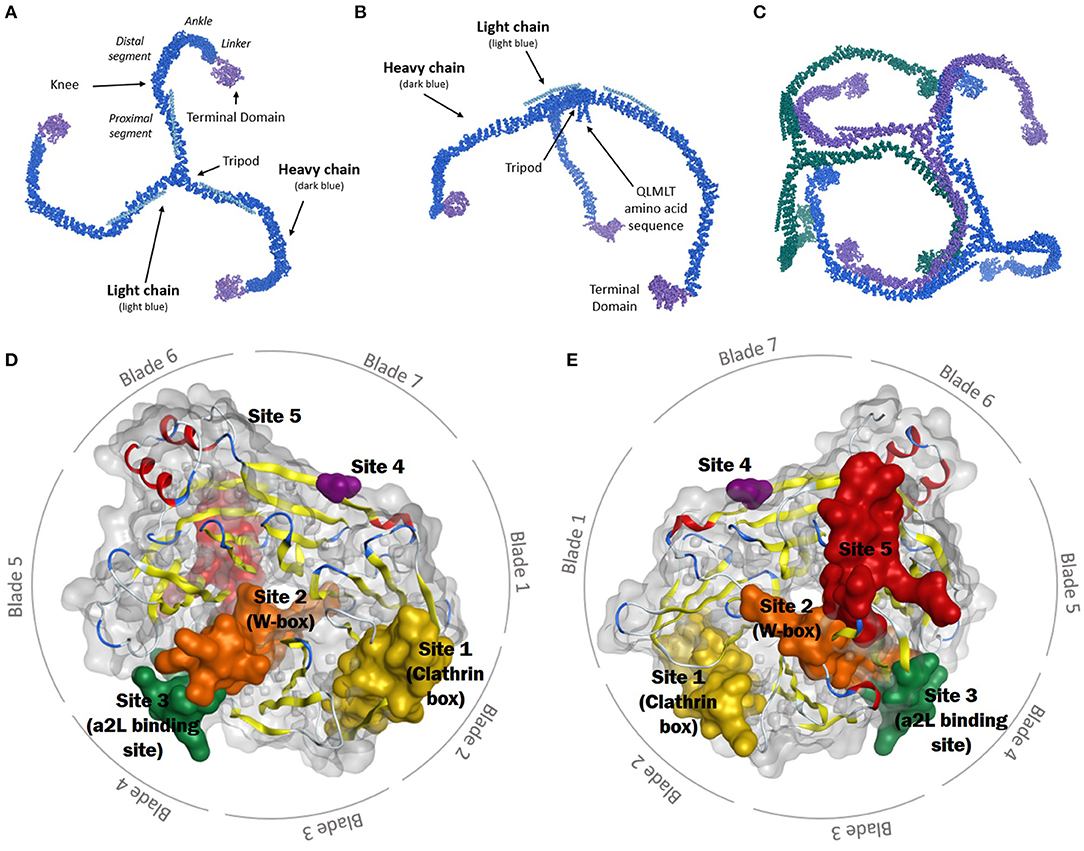
Frontiers Role of Clathrin and Dynamin in Clathrin Mediated Endocytosis/Synaptic Vesicle Recycling and Implications in Neurological Diseases







