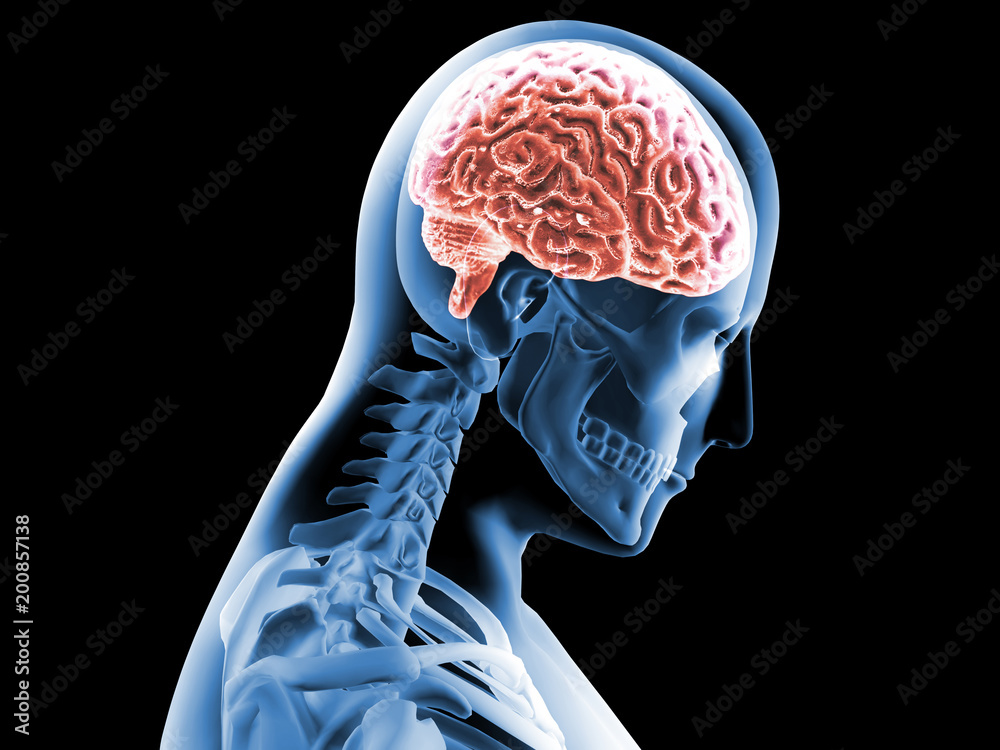
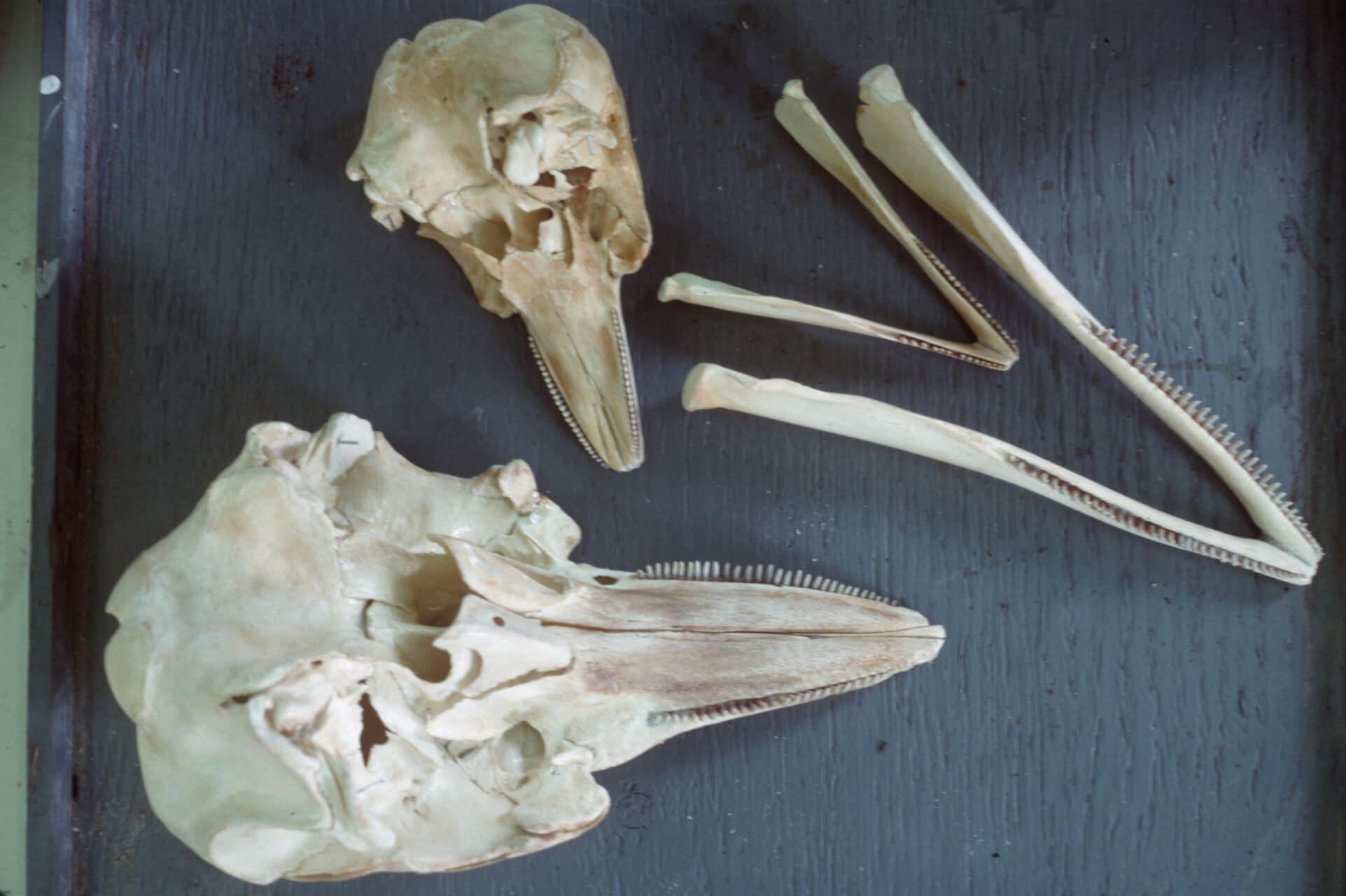
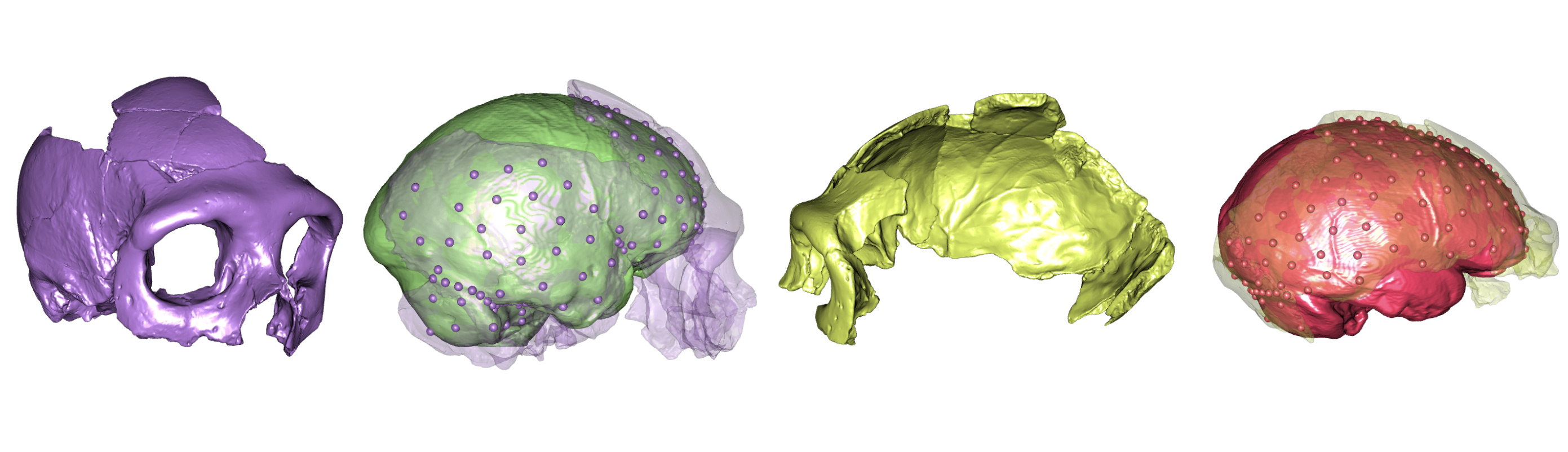
Comparing canine brains using 3-D-endocast modelling

Based on digital endocranial cast models, the canine brain does not increase proportionally with body size. Researchers at ELTE Eötvös Loránd and Kaposvár University in Hungary reconstructed the surface morphology of 28 canine brains, including various dog breeds, wolves, coyotes, and jackals. The shortening of the facial skeleton greatly influences the ratio of certain brain regions, primarily the olfactory bulb and the frontal lobe. These changes may have profound implications for olfactory and problem-solving abilities.
When our evolutionary ancestors first crawled onto land, their brains only half-filled their skulls

PALAEONTOLOGY[online] Article: Patterns in Palaeontology > Patterns In Palaeontology: Digitally Peering Inside Fossil Skulls

The Role of Endocasts in the Study of Brain Evolution - ScienceDirect

Neuroanatomical asymmetry in the canine brain
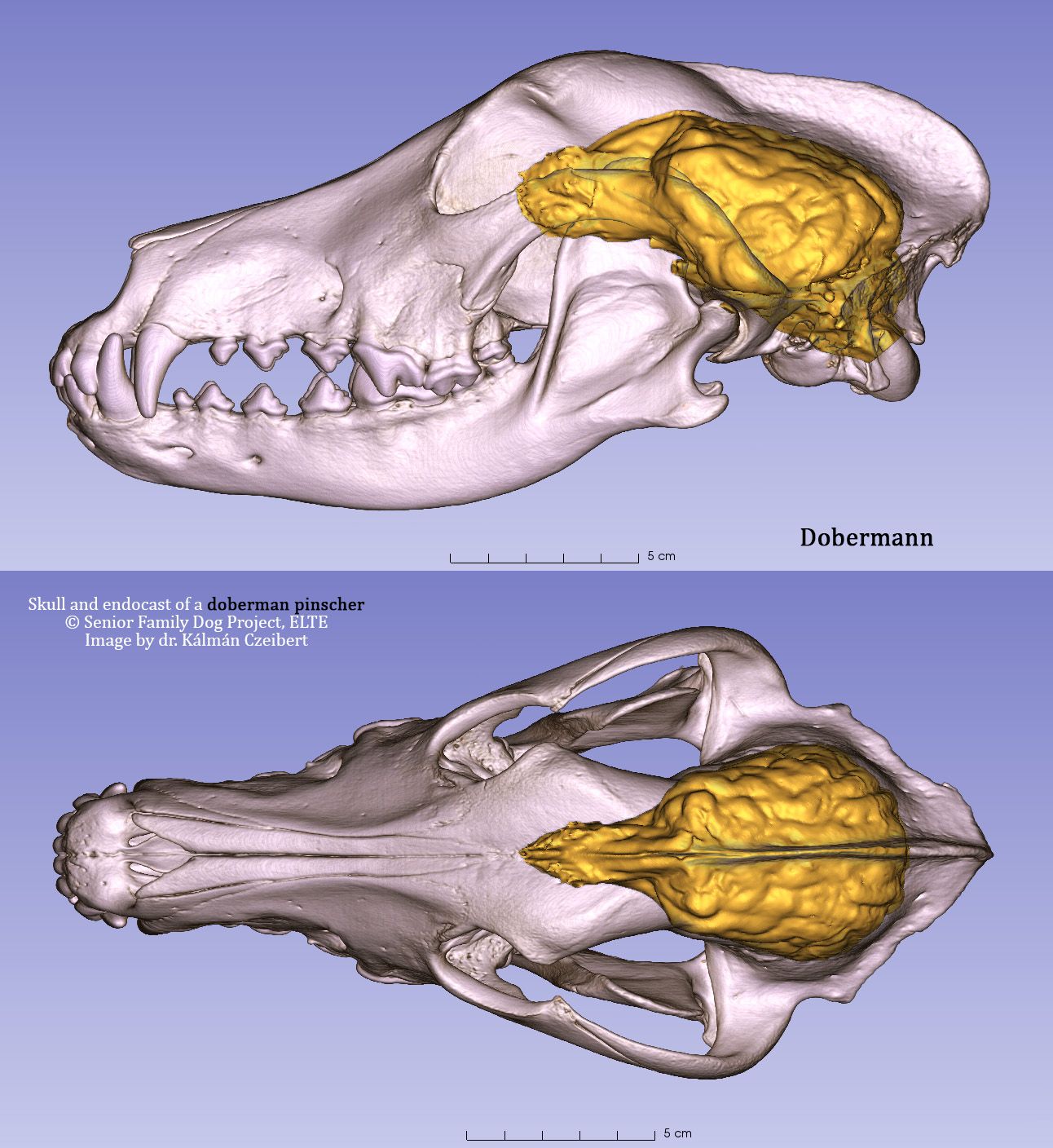
Comparing canine brains using 3D-endocast modelling
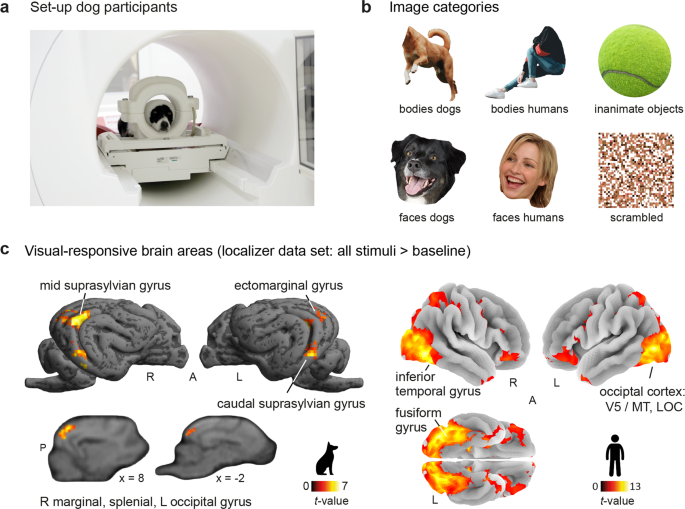
Functionally analogous body- and animacy-responsive areas are present in the dog (Canis familiaris) and human occipito-temporal lobe

Brains The Smithsonian Institution's Human Origins Program
endocast Lawn Chair Anthropology

Human Brain Mapping, Neuroimaging Journal
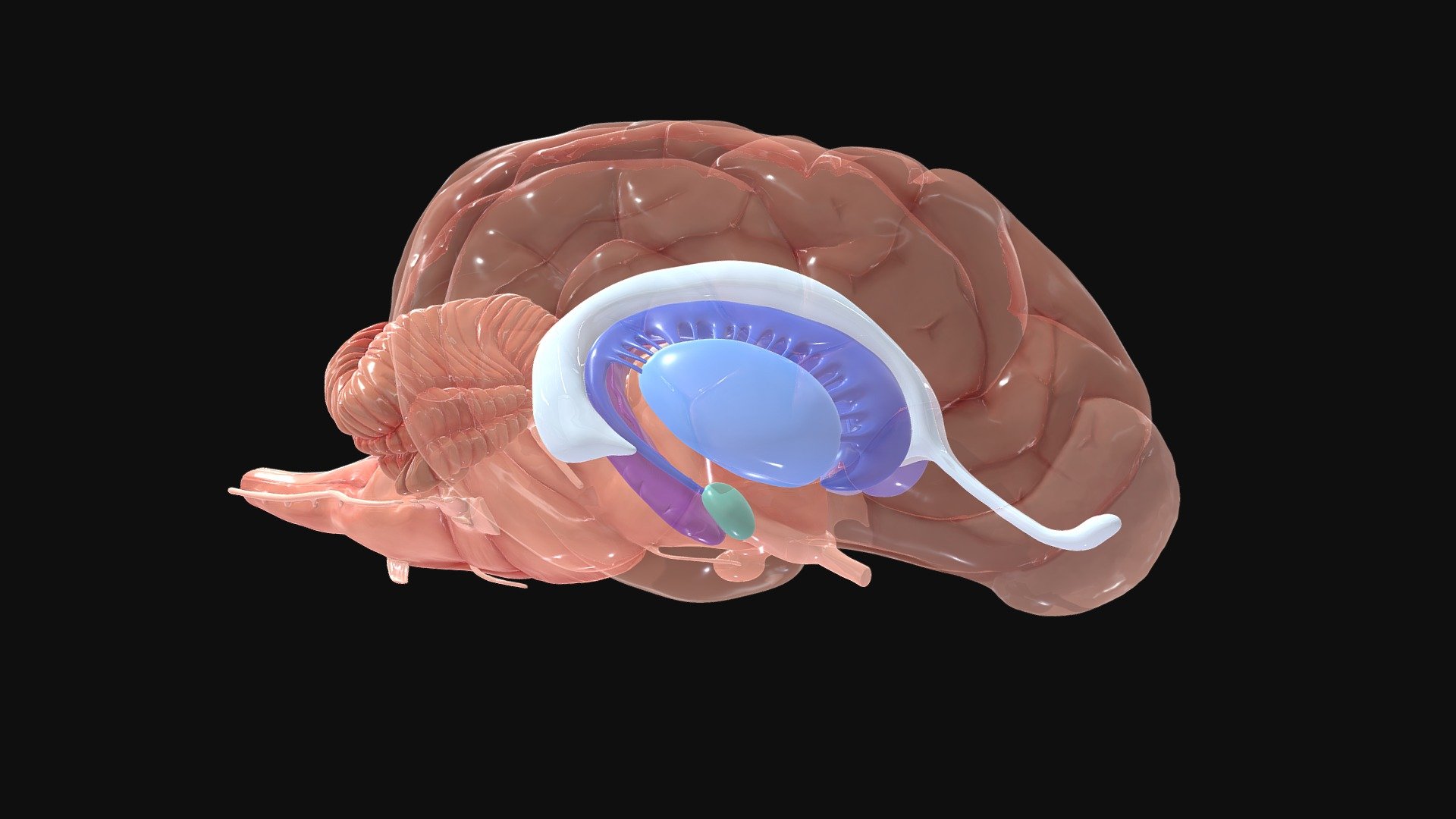
Canine Brain Internal Cerebral Structures - 3D model by ERC (@ERC) [b7e42bc]

Skulls and brains – paleoneurology
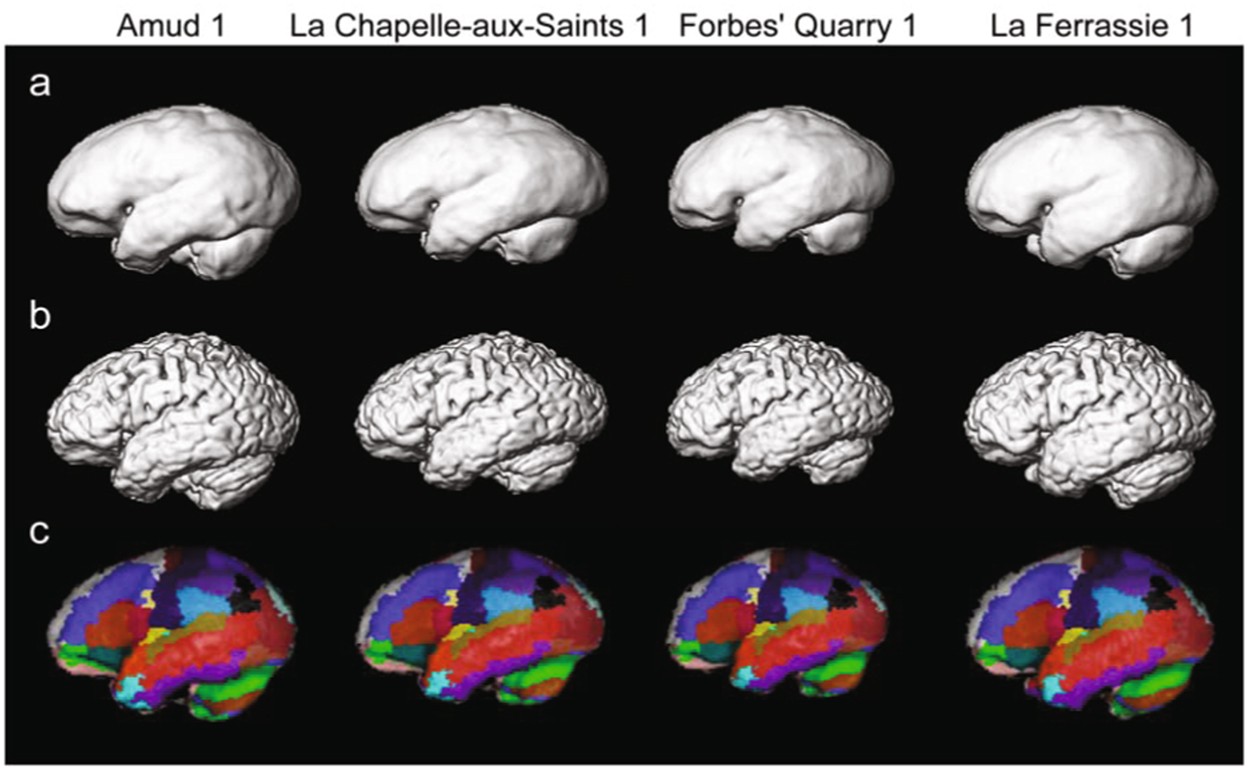
Reconstructing the Neanderthal brain using computational anatomy
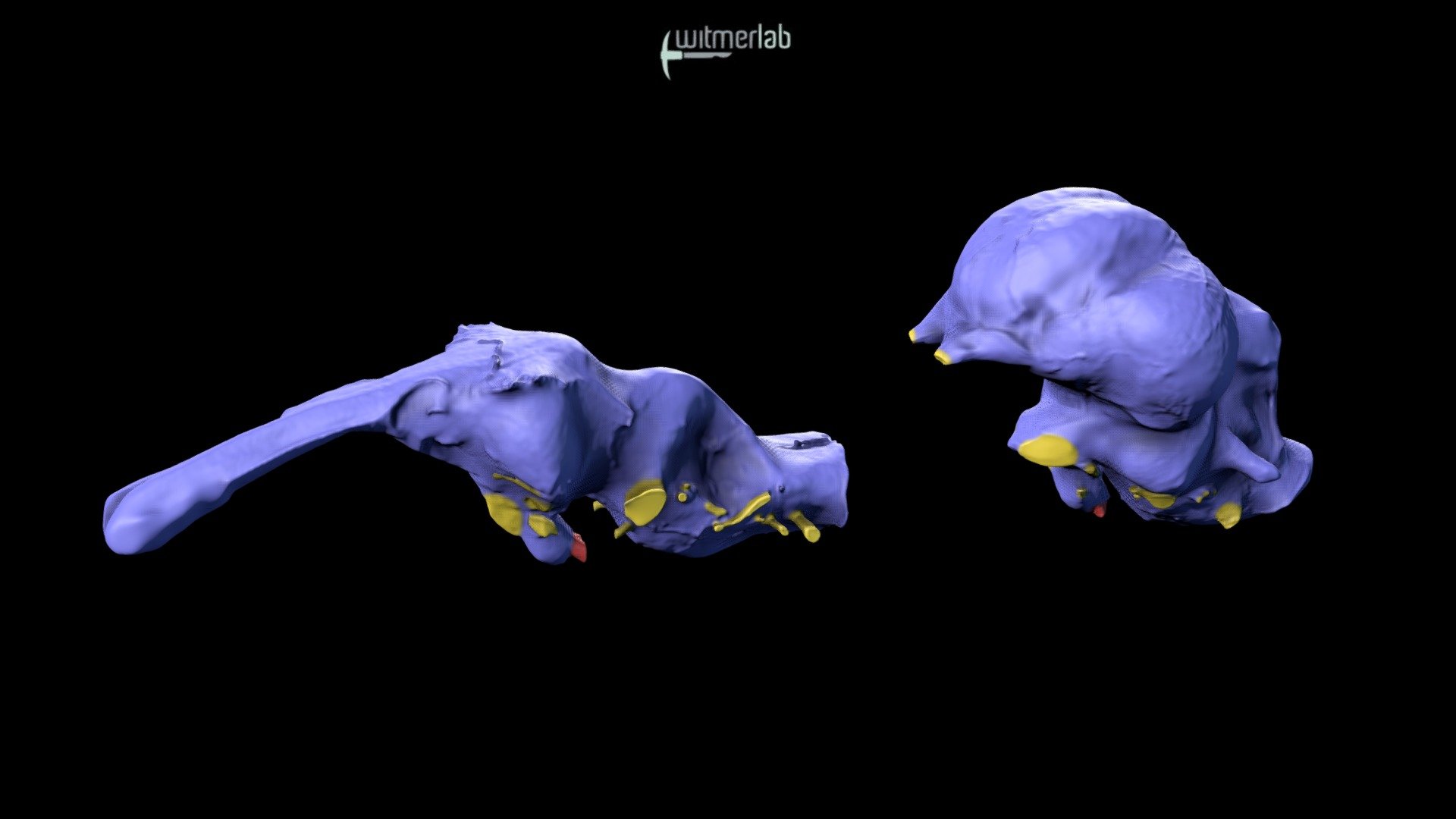
Brain endocasts of alligator & ostrich compared - Download Free 3D model by WitmerLab at Ohio University (@witmerlab) [cd79cdd]