Evaluating coverage bias in next-generation sequencing of Escherichia coli
Whole-genome sequencing is essential to many facets of infectious disease research. However, technical limitations such as bias in coverage and tagmentation, and difficulties characterising genomic regions with extreme GC content have created significant obstacles in its use. Illumina has claimed that the recently released DNA Prep library preparation kit, formerly known as Nextera Flex, overcomes some of these limitations. This study aimed to assess bias in coverage, tagmentation, GC content, average fragment size distribution, and de novo assembly quality using both the Nextera XT and DNA Prep kits from Illumina. When performing whole-genome sequencing on Escherichia coli and where coverage bias is the main concern, the DNA Prep kit may provide higher quality results; though de novo assembly quality, tagmentation bias and GC content related bias are unlikely to improve. Based on these results, laboratories with existing workflows based on Nextera XT would see minor benefits in transitioning to the DNA Prep kit if they were primarily studying organisms with neutral GC content.
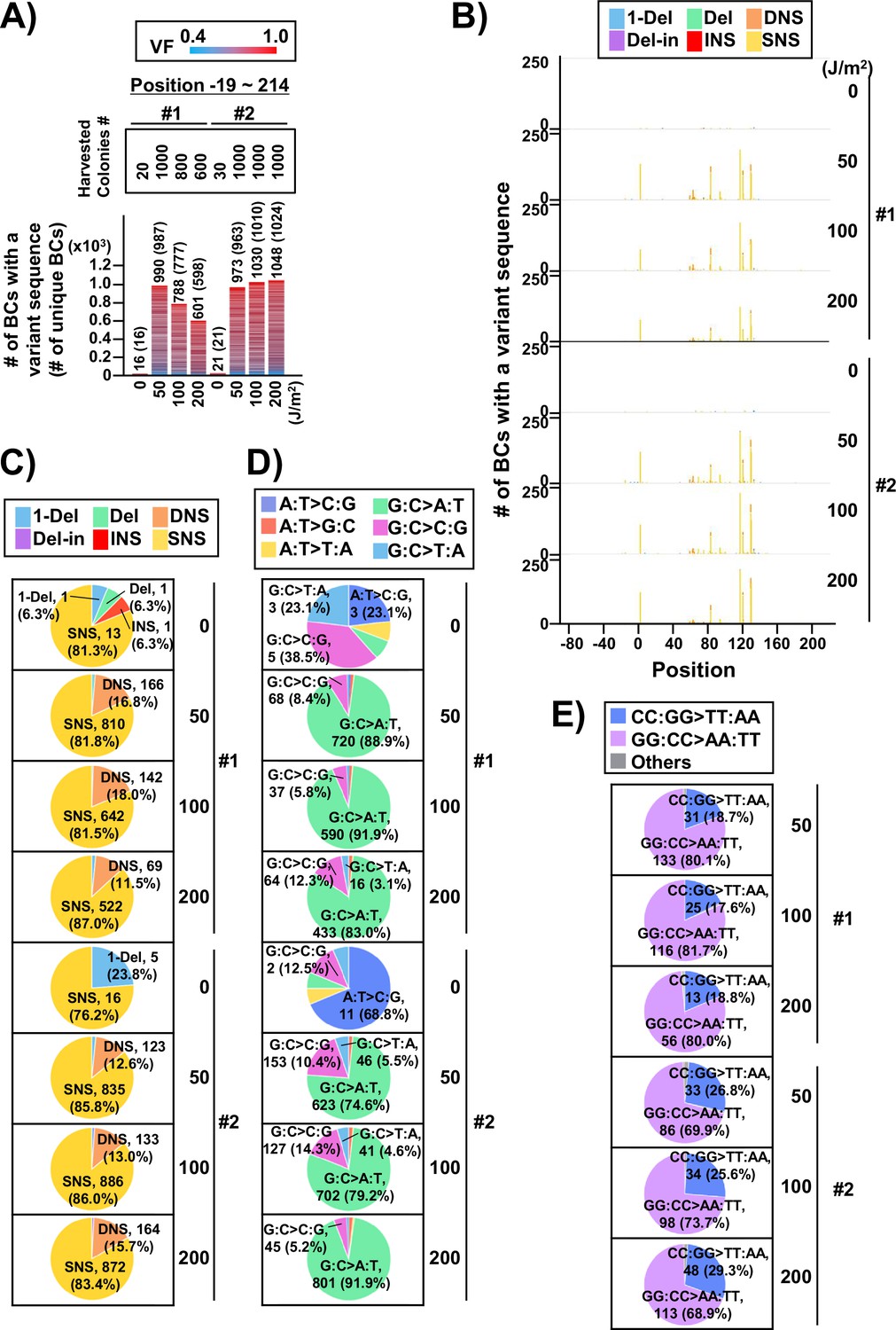
Development of a versatile high-throughput mutagenesis assay with multiplexed short-read NGS using DNA-barcoded supF shuttle vector library amplified in E. coli

Reference-based read clustering improves the de novo genome assembly of microbial strains - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
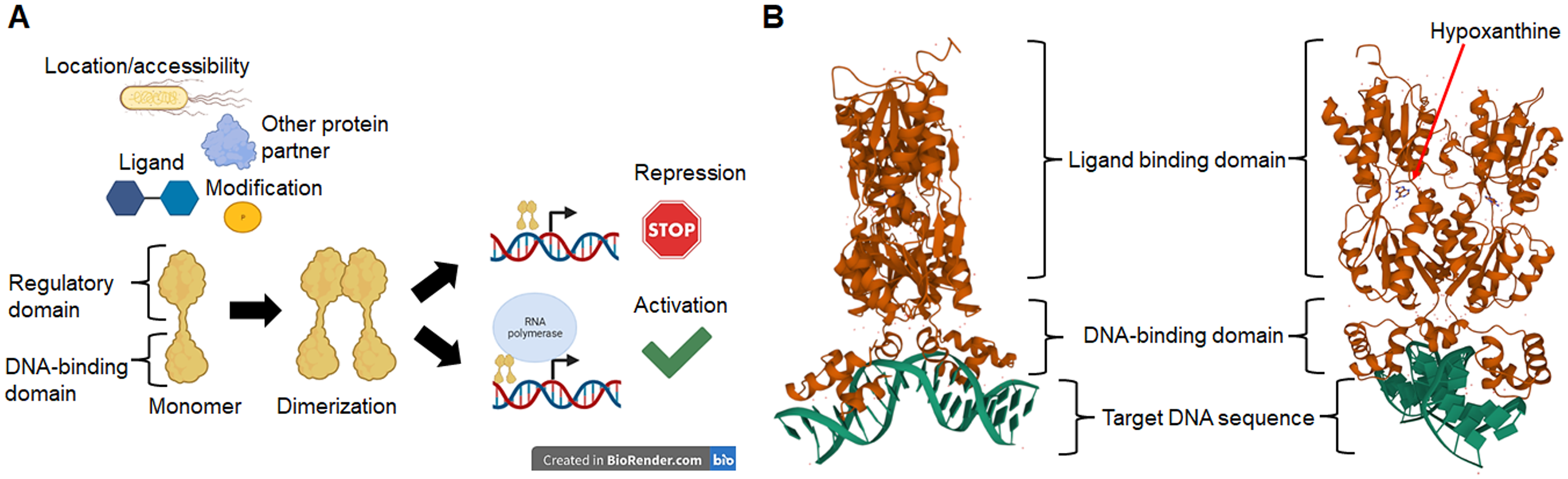
Escherichia coli transcription factors of unknown function: sequence features and possible evolutionary relationships [PeerJ]

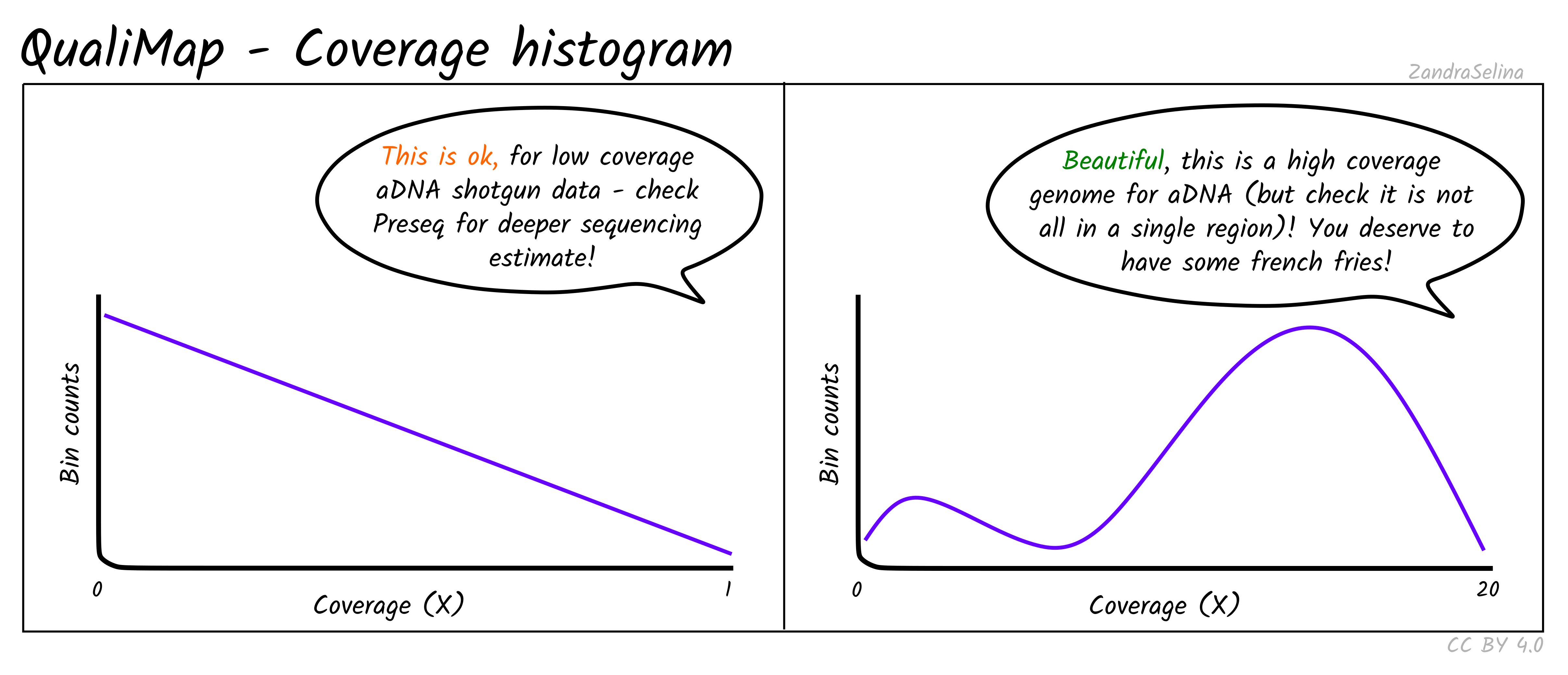
Number of blind spots uniquely present or absent in each sequencing
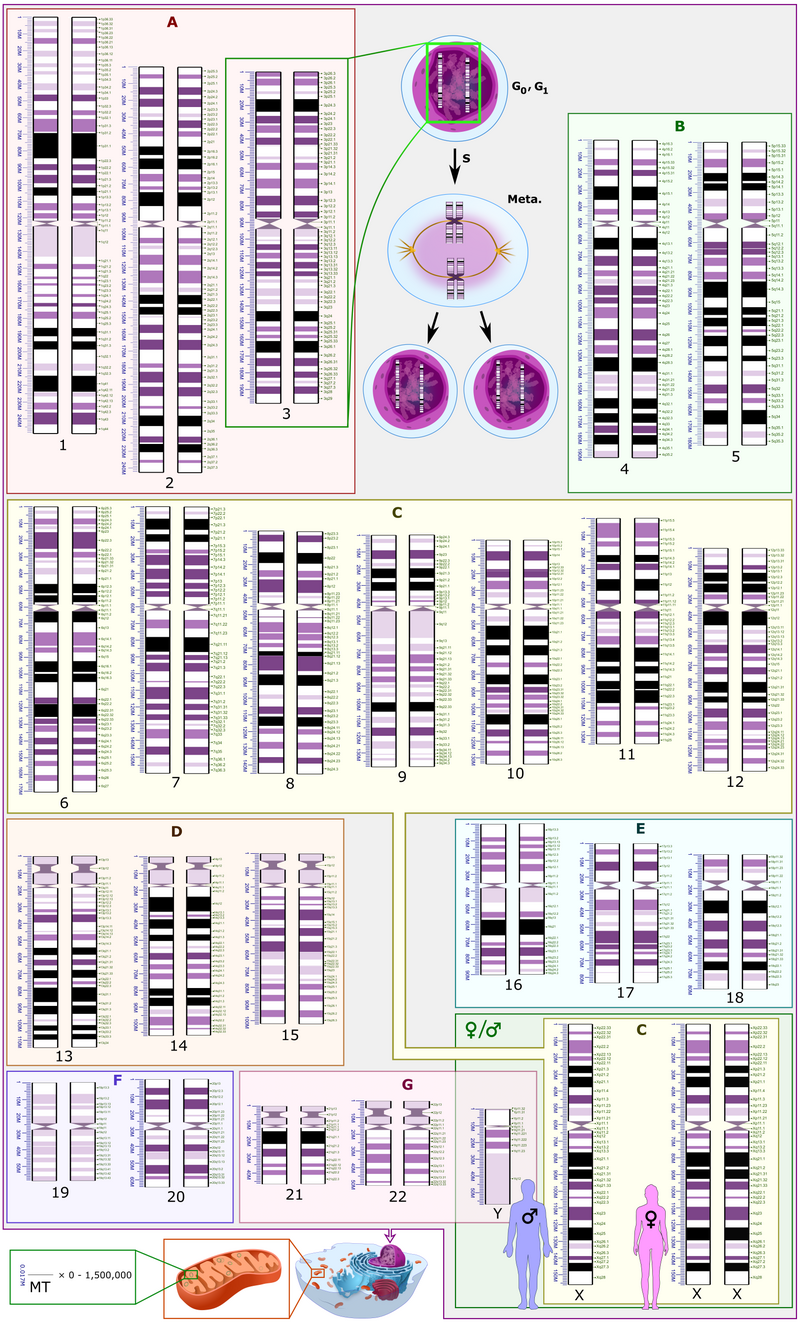
Human genome - Wikipedia

Understanding and controlling for sample and platform biases in NGS assays
Molecular identification of plants: from sequence to species

PDF] Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high-throughput sequencing

PDF] Comparison of the sequencing bias of currently available library preparation kits for Illumina sequencing of bacterial genomes and metagenomes
GC biases in NextSeq, PacBio, Nanopore, and HiSeq data. The dot plots

Variance of allele balance calculated from low coverage sequencing data infers departure from a diploid state, BMC Bioinformatics

Non-uniformity in genome coverage and its impact on the sequencing

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

PDF] Illuminating Choices for Library Prep: A Comparison of Library Preparation Methods for Whole Genome Sequencing of Cryptococcus neoformans Using Illumina HiSeq