Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

Urban warming and future air-conditioning use in an Asian megacity: importance of positive feedback

Meteorological statistics for all days (x), clear-sky days (circles)

Plots of average diurnal cycles of the observed total CO2 flux, ORF

Temperatures and heat fluxes in the single-layer UCM. T a is the

Building heat budget and its response to ΔT in the case of buildings

COVID-19-induced low power demand and market forces starkly reduce CO2 emissions

Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

Spatial distribution of August monthly mean surface air temperature

Air quality and urban climate improvements in the world's most populated region during the COVID-19 pandemic - IOPscience

Distribution of urban parameters: (a)-(c) urban-area ratio, (f)-(h)
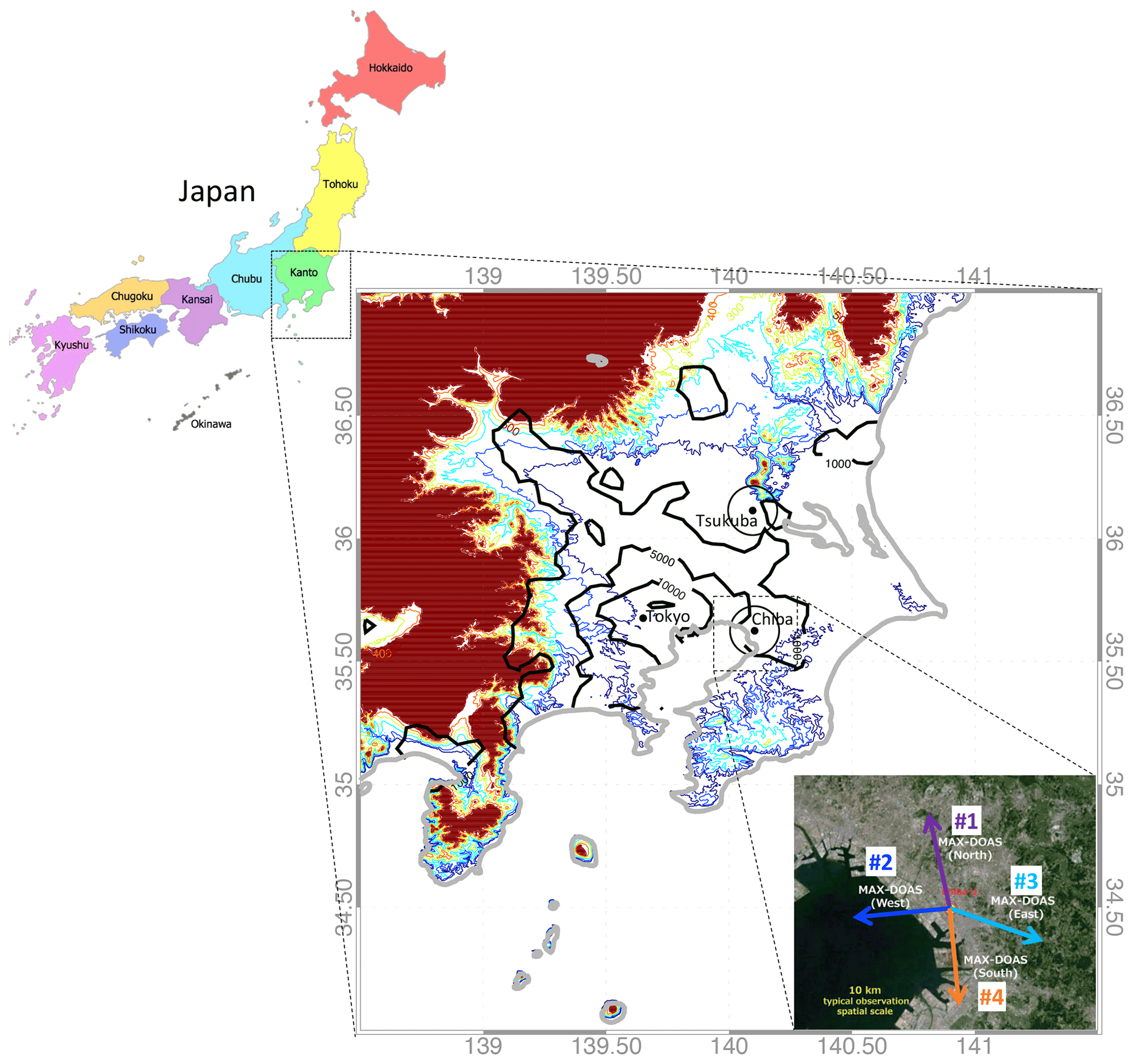
ACP - Peculiar COVID-19 effects in the Greater Tokyo Area revealed by spatiotemporal variabilities of tropospheric gases and light-absorbing aerosols

Spatial distribution of the projected increase (future 2050s minus

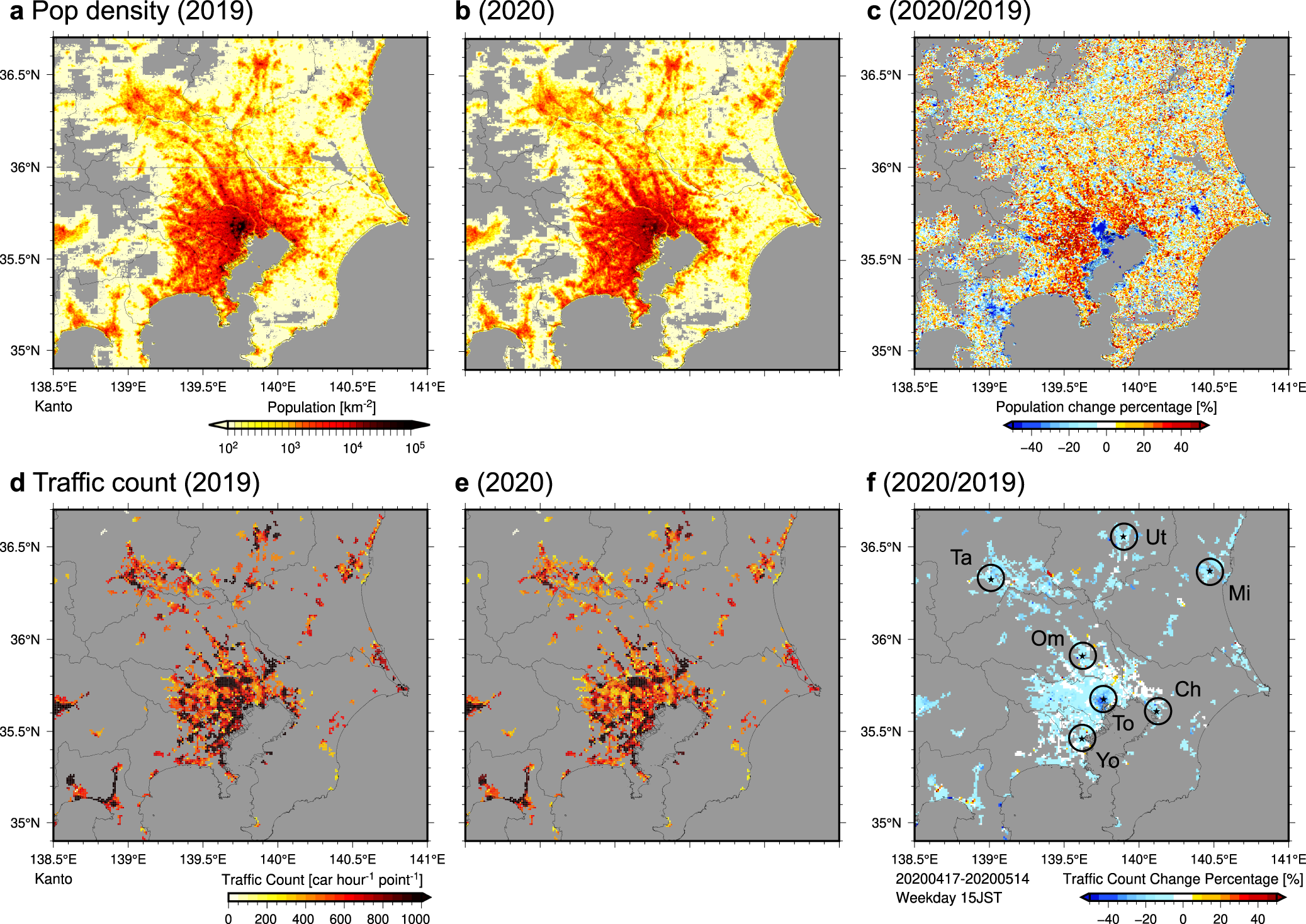
Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data
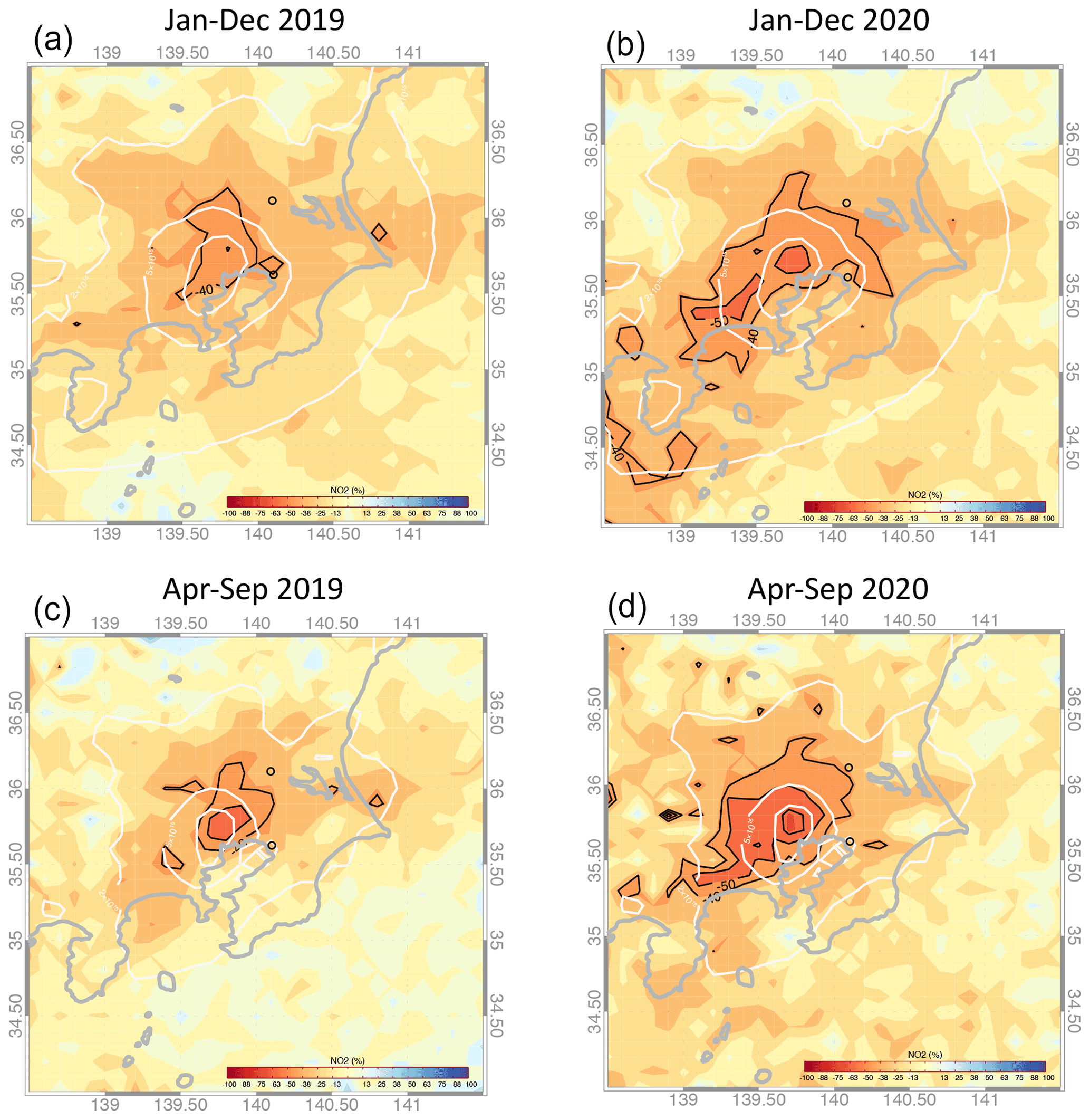
ACP - Peculiar COVID-19 effects in the Greater Tokyo Area revealed by spatiotemporal variabilities of tropospheric gases and light-absorbing aerosols

Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data





:format(webp)/https://static-sg.zacdn.com/p/gap-2726-0542533-1.jpg)

