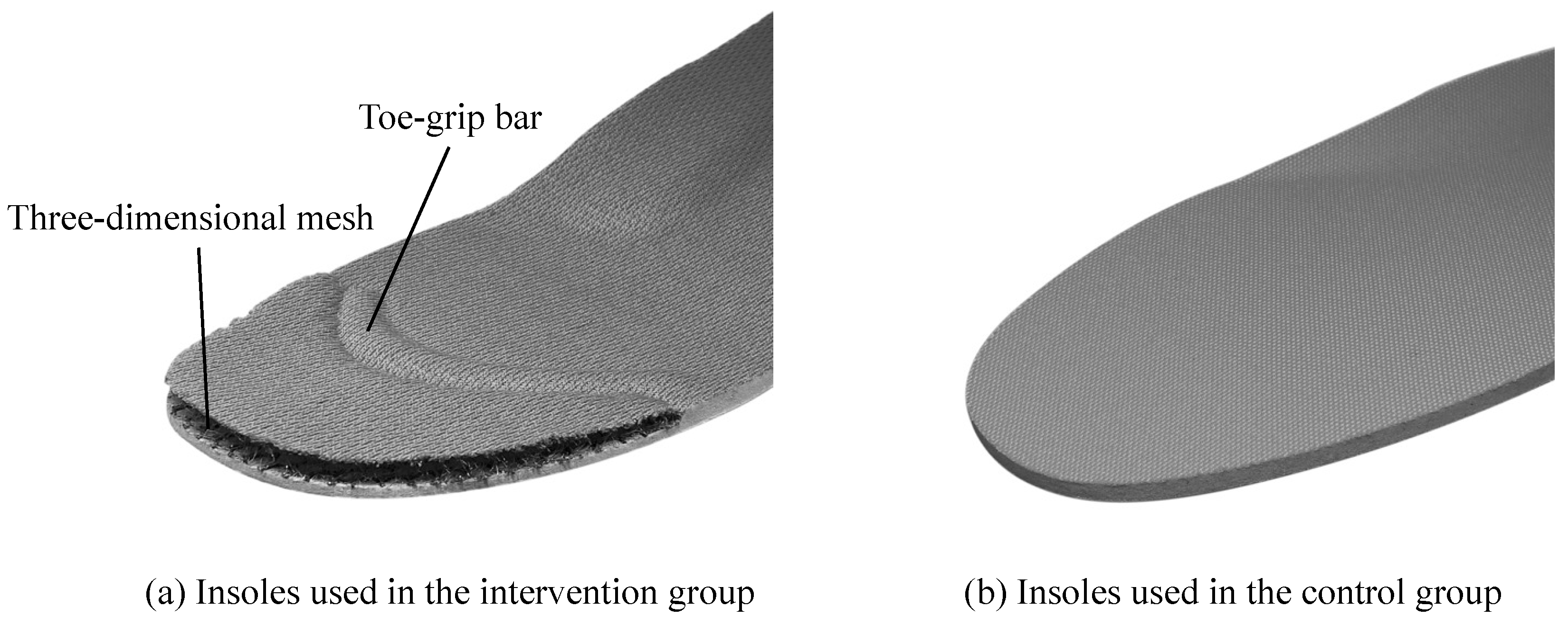
Toe grip force of the dominant foot is associated with fall risk in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study, Journal of Foot and Ankle Research
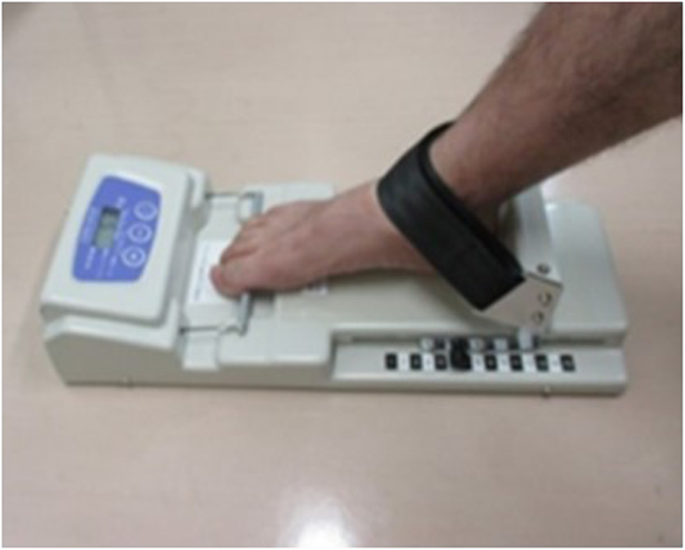

Toe grip force of the dominant foot is associated with fall risk in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study, Journal of Foot and Ankle Research

CSM 2012 SOWH Posters, Article

Reference values for toe grip strength among Japanese adults aged 20 to 79 years: a cross‐sectional study - Uritani - 2014 - Journal of Foot and Ankle Research - Wiley Online Library

The Evidence-Based Guide to Grip Strength Training & Forearm Muscle Development • Stronger by Science

Clinical practice guideline for the assessment and prevention of falls
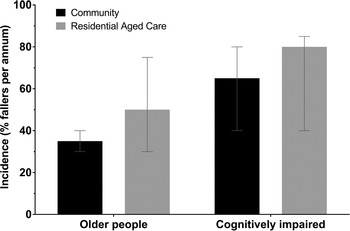
Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Falls (Part I) - Falls in Older People
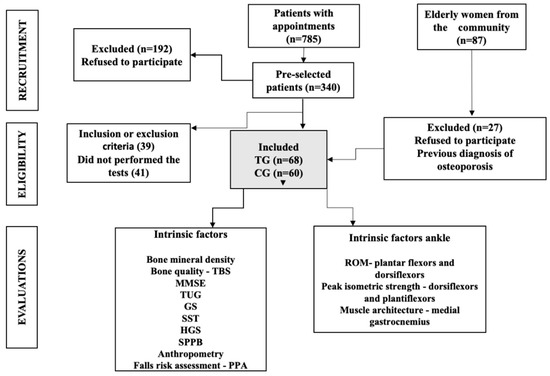
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

Comparison of toe pressure strength in the standing position and toe grip strength in association with the presence of assistance in standing up: a cross-sectional study in community-dwelling older adults

Lower-Limb Factors Associated with Balance and Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Clinical Synthesis in: Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association Volume 110 Issue 5 (2020)

PDF] Falls and fall prevention in community-dwelling older adults

PDF) Feet/Footwear-Related Fall Risk Screening Tool for Older Adults: Development and Content Validation

Lower-Limb Factors Associated with Balance and Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Clinical Synthesis in: Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association Volume 110 Issue 5 (2020)

Why do older adults stand-up differently to young adults?: investigation of compensatory movement strategies in sit-to-walk