Prevalence and correlates of psychological distress among 13–14 year old adolescent girls in North Karnataka, South India: a cross-sectional study, BMC Public Health
Background Mental health disorders among adolescents have emerged as a major public health issue in many low and middle-income countries, including India. There is a paucity of research on the determinants of psychological distress, particularly among the poorest girls in the poorest communities. The purpose of this study was to assess the prevalence and correlates of different indicators of psychological distress among 13–14 year old low caste girls in rural, south India. Methods Cross-sectional survey of 1191 low caste girls in two districts in north Karnataka, conducted as part of a cluster randomised-control trial. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis assessed correlates of different indicators of psychological distress. Results More than one third of girls (35.1%) reported having no hope for the future. 6.9% reported feeling down, depressed or hopeless in the past 2 weeks. 2.1% reported thinking they would be better off dead or of hurting themselves in some way in the past 2 weeks. 1.6% reported sexual abuse, 8.0% rrecent eve teasing and 6.3% having no parental emotional support. Suicidal ideation was independently associated with sexual abuse (AOR 11.9 (3.0–47.0)) and a lack of parental emotional support (AOR 0.2 (0.1–0.5)). Feeling down, depressed or hopeless was independently associated with recent eve-teasing (AOR 2.9 (1.6–5.4)), a harassing or abusive school environment (AOR 3.9 (1.8–8.2)), being frequently absent (AOR 2.8 (1.5–5.5)) or having dropped out of school (AOR 2.1 (1.0–4.3)), and living in Vijayapura district (AOR 2.5 (1.6–4.1)). Having no hope for the future was independently associated with a range of factors, including recent “eve-teasing” (AOR 1.5 (1.0–2.4)), being engaged (AOR 2.9 (0.9–9.7)), not participating in groups (AOR 0.5 (0.4–0.6)) and a lack of emotional support (AOR 0.6 (0.4–0.7)). Conclusions Rather than being a time of optimism, a third of low caste girls in rural north, Karnataka have limited hope for the future, with some contemplating suicide. As well as having important development benefits, interventions that address the upstream structural and gender-norms based determinants of poor mental health, and provide adolescent services for girls who require treatment and support, should have important benefits for girls’ psychological wellbeing. Trial registration Prospectively registered at ClinicalTrials.GovNCT01996241 . November 27, 2013

Adolescent girls' health, nutrition and wellbeing in rural eastern

April Mazzuca's research works University of British Columbia, Vancouver (UBC) and other places
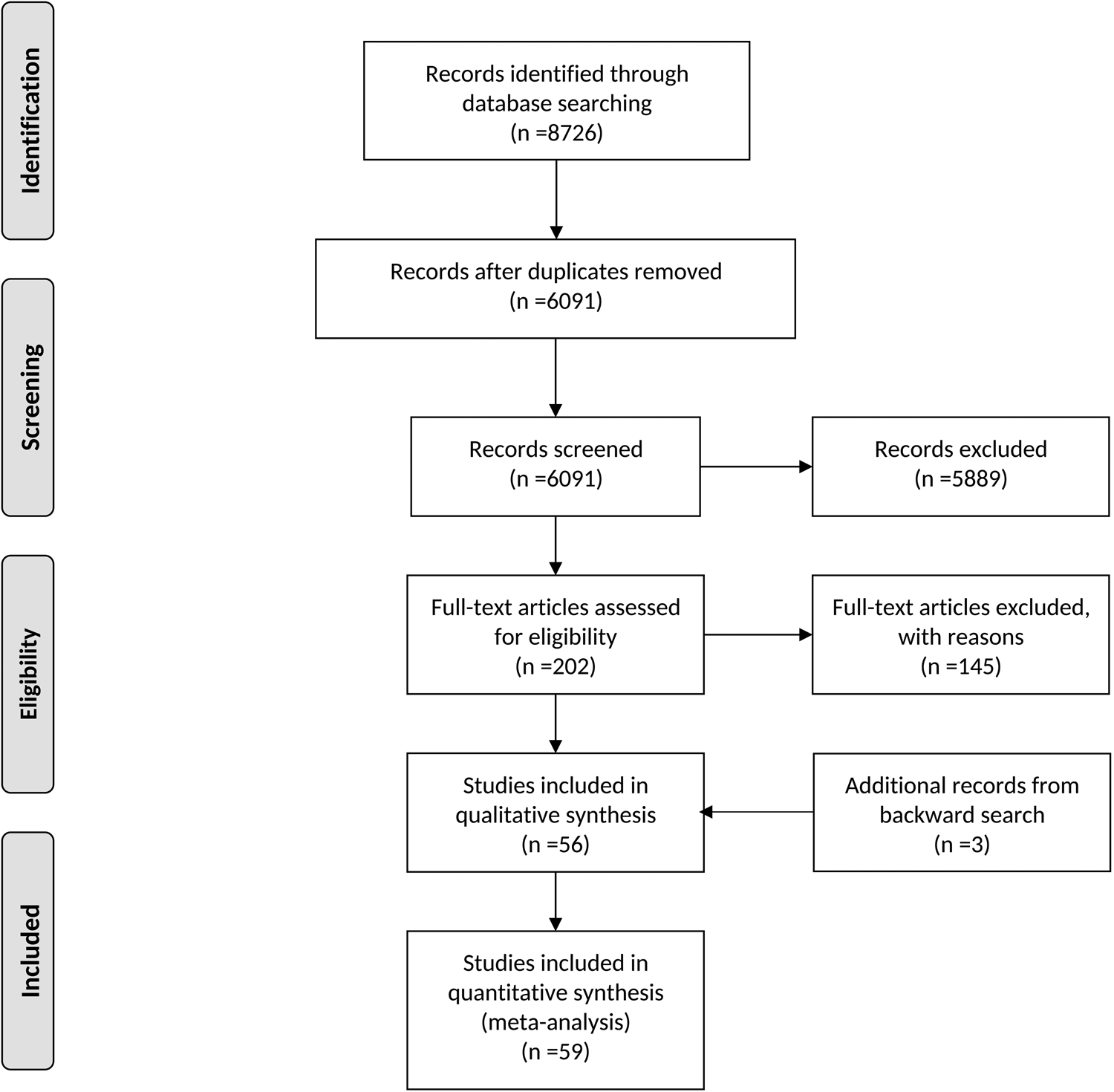
Parental education and youth suicidal behaviours: a systematic
LSHTM Research Online

PDF) Association of Social Network Characteristics with Substance

Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990

Prevalence of child maltreatment in India and its association with gender, urbanisation and policy: a rapid review and meta-analysis protocol. - Abstract - Europe PMC

The burden of mental disorders across the states of India: the

Access to online learning: Machine learning analysis from a social

Adolescent perinatal mental health in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review of qualitative and quantitative evidence - ScienceDirect
Full article: Association between gender disadvantage factors and

Unequal Gender Norms Are Related to Symptoms of Depression Among

Unequal Gender Norms Are Related to Symptoms of Depression Among

Gender differences in psychosocial status of adolescents during