Slope of graph of compressibility factor(Z) with pressure(P) for hydrogen gas at any pressure i
Slope of graph of compressibility factor(Z) with pressure(P) for hydrogen gas at any pressure i
Slope of graph of compressibility factor-Z- with pressure-P- for hydrogen gas at any pressure i
-(1)-300.jpg)
Difference Between Ideal Gas And Real Gas - GeeksforGeeks

Compressibility factor - Wikipedia
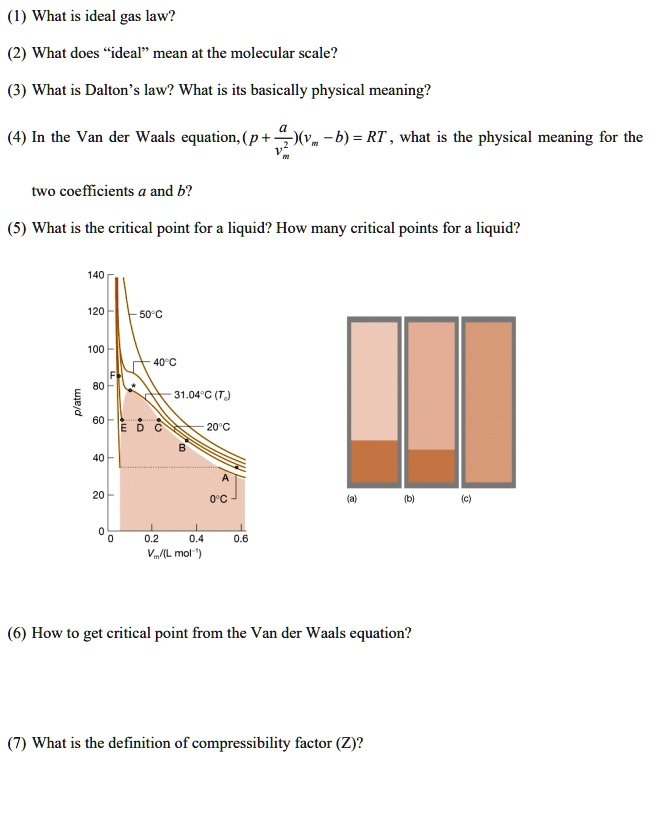
SOLVED: (1) What is the ideal gas law? (2) What does ideal mean at the molecular scale? (3) What is Dalton's law? What is its basic physical meaning? (4) What are the

variations of 2 12.7 (a) eb (c)-(ar (d) - 6. The given graph represent the variations (compressibility factor (Z)=- gases A, B and C. Identify the only incorrect statement pl) versus p

A new empirical model and neural network-based approach for evaluation of isobaric heat capacity of natural gas - ScienceDirect

Assertion :Compressibility factor (Z) non ideal gases is always greater than 1. Reason: Non-ideal gases always exert higher pressure than expected.Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation
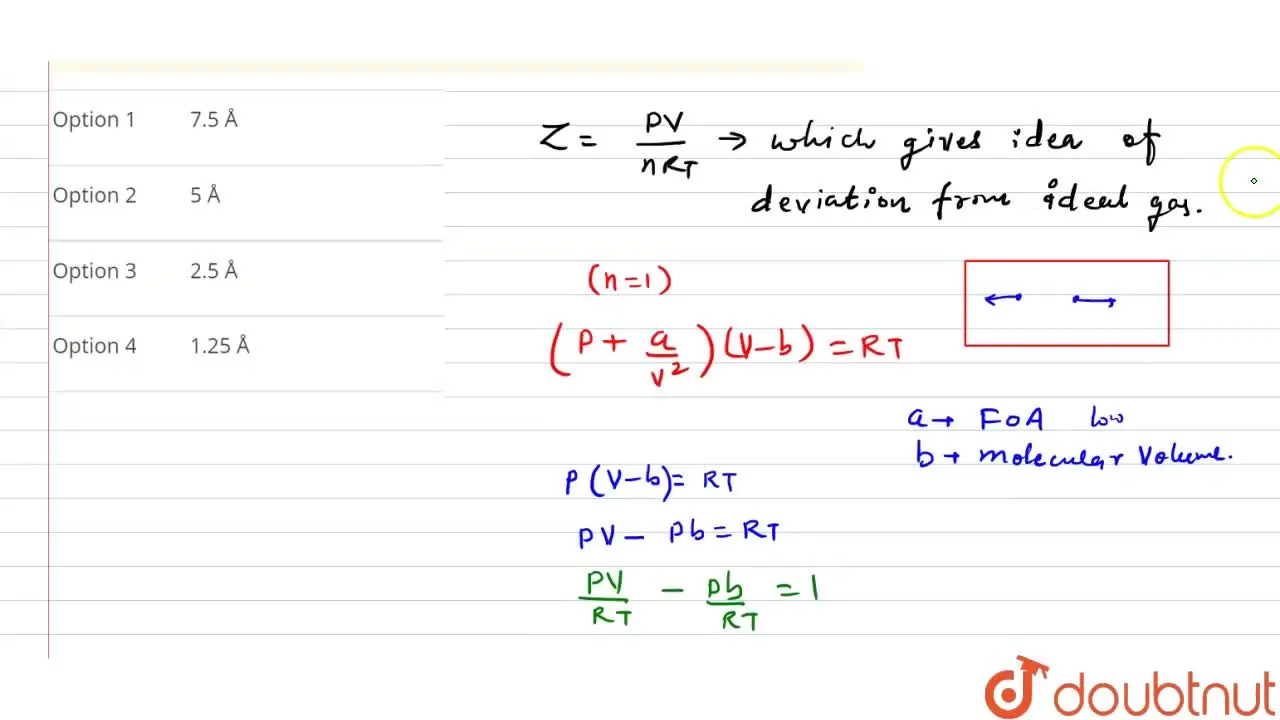
If the slope of 'Z' (compressibility factor) vs. 'p' curve is constant
Energies, Free Full-Text

Deviation of real gas from ideal behaviour

Compressibility factor z versus 100/V, for several values of Pressure

The graph of compressibility factor (Z) vs. P for one mole of a real gas is shown in following
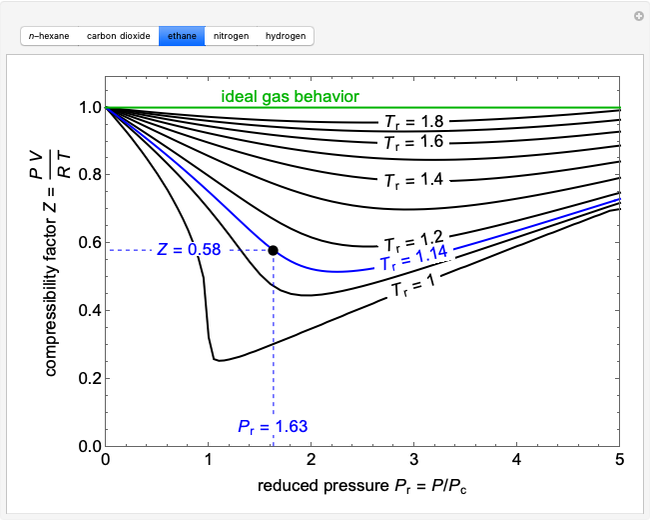
Compressibility Factor Charts - Wolfram Demonstrations Project

A real gas M behaves almost like an ideal gas. Graph 1 is obtained by plotting volume, V against temperature, T for x mol of gas M at pressure, P_1. a. Suggest
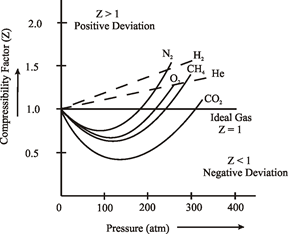
Chemistry Desk: Effect of Pressure




